Figure 1.
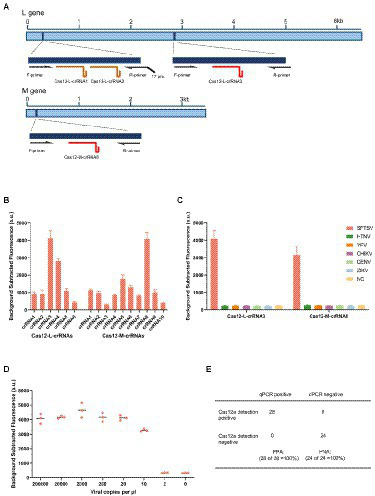
Establishment of detection method for SFTSV based on CRISPR/Cas12a. (A) Schematic diagram of the L gene and M gene of SFTSV. The gene map shows the location of selected regions, corresponding primers and crRNAs. T7 pro, T7 polymerase promoter. (B) The designed LbaCas12a-crRNAs detect the targets of L gene and M gene that were amplified using the respective primer mix. The Cas12-L-crRNA3 and Cas12-M-crRNA8 showed stronger signals using the same protocol. Values represent mean ± SD (n = 3). (C) SFTSV, Hantaan virus, Yellow fever virus, Chikungunya virus, Dengue virus, and Zika virus were detected parallelly by Cas12-L-crRNA3 or Cas12-M-crRNA8. Only the RNA from SFTSV produced detected signals, whereas RNAs from other viruses and the negative control did not produce any change of signals. NC, no-template control. Values represent mean ± SD (n = 3). (D) The limit of detection for Cas12a-based assay using Cas12-M-crRNA8. The diluted SFTSV RNA standards were used as detection targets (n = 3). (E) Comparison of the clinical performance of Cas12a-based assay and qPCR assay. A total of 52 clinical samples (28 positives and 24 negatives) were evaluated using the fluorescent version of CRISPR/Cas12a assay and qPCR assay; PPA, percent positive agreement. PNA, percent negative agreement.
