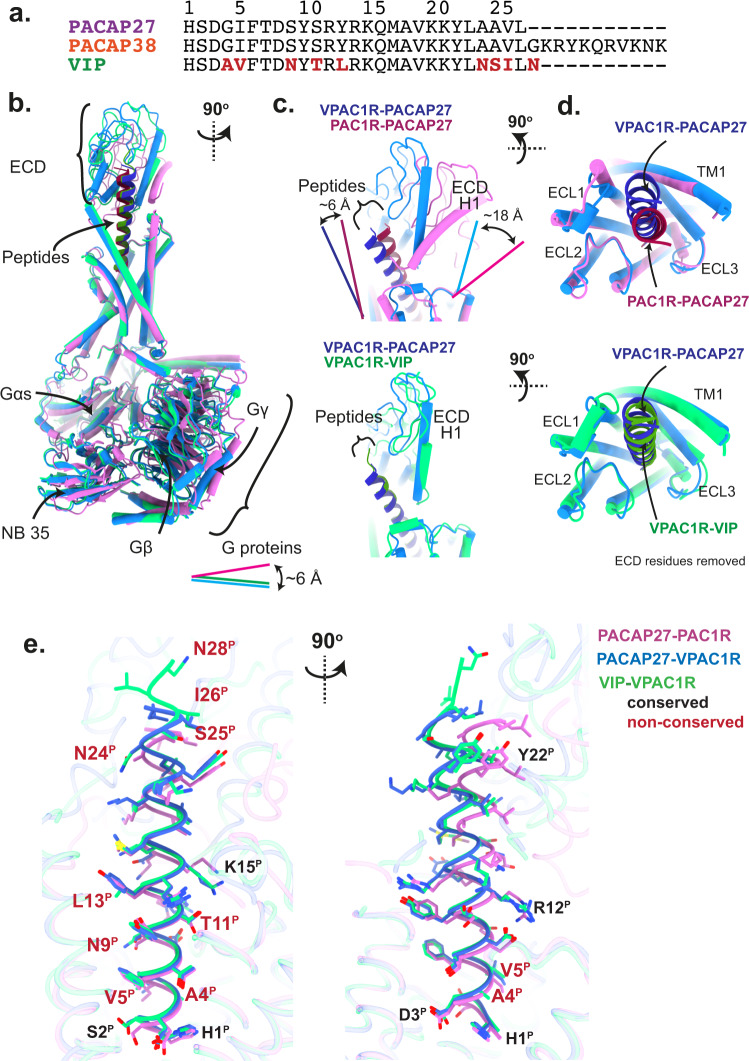
Fig. 1. Overview of active, Gs-coupled PACAP family complexes solved using cryo-EM.
a Sequence alignment of endogenous PACAP family peptides PACAP27, PACAP38 and VIP, with non-conserved VIP residues shown in red. b–d Secondary structure comparison of Gs complexes of PAC1R-PACAP27 (pink, peptide: dark red), VPAC1R-VIP (light green, peptide: dark green) and VPAC1R-PACAP27 (light blue, peptide: dark blue). Secondary structure is shown as ribbon for the peptide helix and as cylinders (helices) and beta sheets for the rest of the complex. Complexes are shown in different angles as front view of the entire complex (b, all three structures), side view of the extracellular domain (ECD) and peptide C-terminus (c, PACAP27 bound structures top panel, VPAC1R structures bottom panel) and top view of the receptor bundle, extracellular loops (ECL) and peptide C-terminus (d, PACAP27 bound structures top panel, VPAC1R structures bottom panel, with ECD residues removed for clarity). Offsets between VPAC1R and PAC1R structures of ECD helix 1 (H1, C-terminus), G proteins (Gs αN N-terminus) and peptides (C-terminus) are indicated by lines with distances reported in Å (distance measured between Cα atoms of terminal residues). e Overview of peptide residues within the receptor complexes (receptor-aligned), shown as front and side view (left and right, respectively) with receptor backbone displayed in transparent ribbon format and peptide backbone in ribbon format with sidechains displayed in stick format. Residues labelled in red are VIP residues not conserved with PACAP (as noted in (a)).