Figure 1.
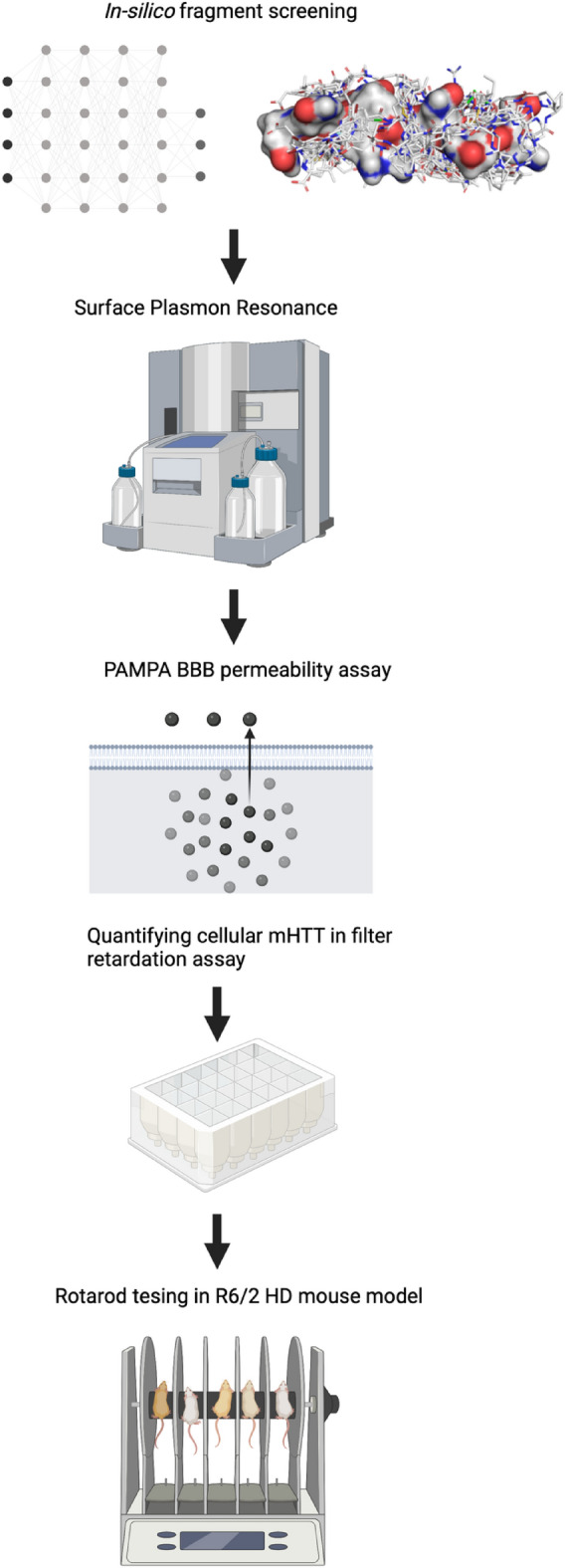
In the first step, we conducted an in-silico-based drug screening with a deep artificial neuronal network. Depicted are the selection of 67 small molecules docked on the surface of the polyQ tract peptide. 40 compounds were tested for their actual binding affinity to mutant huntingtin (mHTT) with Biacore, a system using surface plasmon resonance. Next, compounds were tested in an in-vitro mHTT assay and selected based on the ability of the compounds to lower mHTT and overcome an artificial blood–brain barrier in the PAMPA BBB permeability assay. Finally, we demonstrated in the R6/2 Huntington disease (HD) mouse model that the preclinical candidate GLYN122 can improve motor symptoms as measured with rotarod. Created with BioRender.com.
