Figure 2.
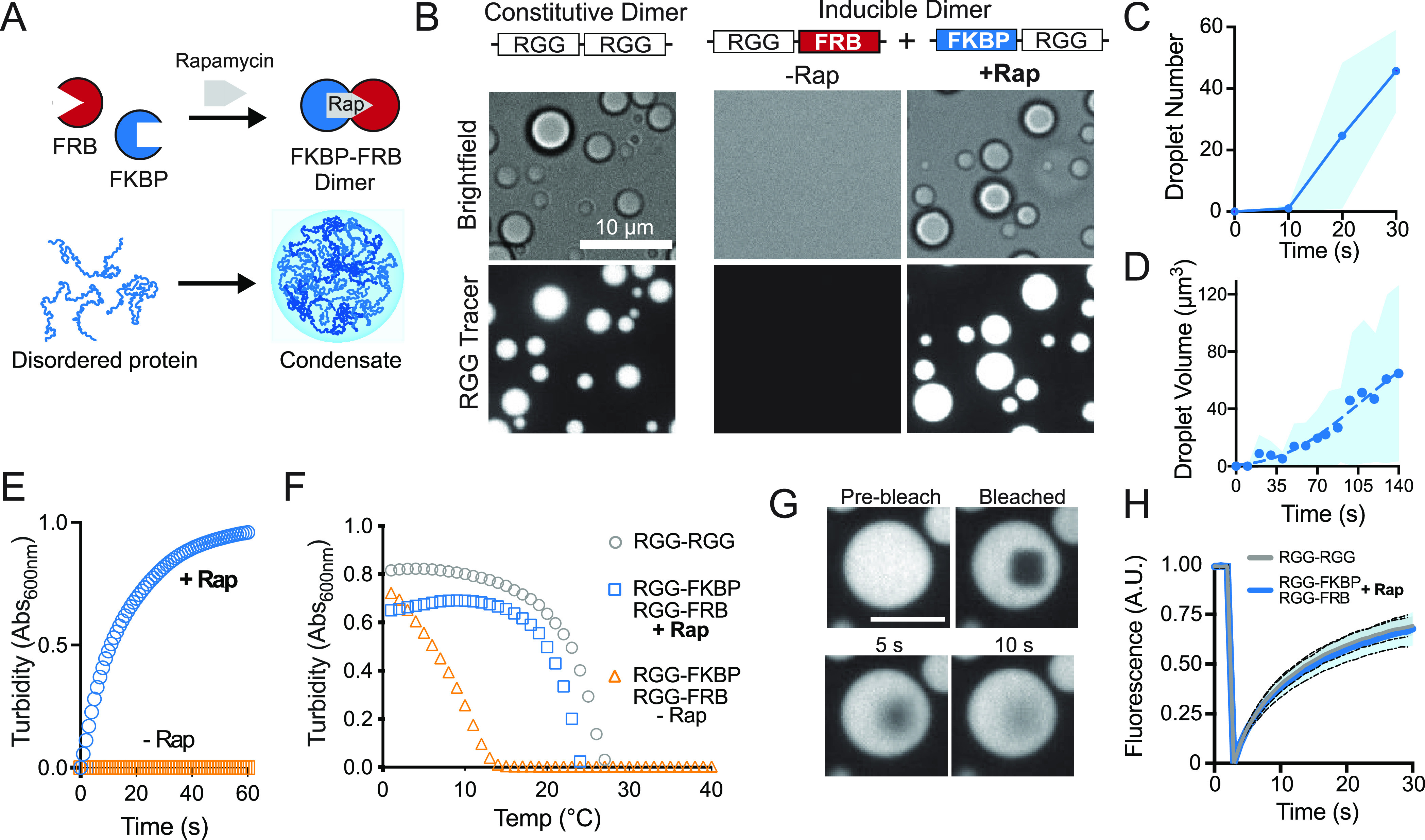
Temporal control of IDR multimerization and phase separation in vitro. (A) Schematic representation for chemogenic dimerization of RGG polypeptides to form mesoscale liquid-like protein condensates. (B) Representative images of liquid droplet formation through increased domain valency upon addition of dimerizer, Rap. Recombinant RGG-FKBP and RGG-FRB proteins, in the absence of Rap, do not form condensates in a buffer containing 10 μM protein and 0.2 μM tracer (RGG-GFP-RGG). Scale bar, 10 μm. Addition of Rap to the reaction rapidly induces dimerization, causing condensate formation similar to the RGG-RGG constitutive dimer. (C and D) Quantitation of the kinetics of droplet formation upon equimolar addition of Rap. Average of three independent trials. Shaded area, StDev. (E) Kinetics of solution clouding after addition of dimerizer in spectrophotometric turbidity assays; average of three experiments area shown. (F) Phase transition temperature measured by turbidity assay shows induced dimerization of RGG-FKBP and RGG-FRB with Rap shifts the cloud point to higher temperatures, similar to constitutive RGG-RGG dimer; average of three experiments. (G) Representative images from photobleaching and recovery of condensates composed of Rap-mediated RGG-FKBP/RGG-FRB dimers marked by 0.2 μM RGG-GFP-RGG tracer. Scale bar 5 μm. (H) Quantification of FRAP indicating similar recovery kinetics of Rap-induced vs constitutive RGG-RGG dimers. n = 30 condensates from two independent trials.
