Figure 2.
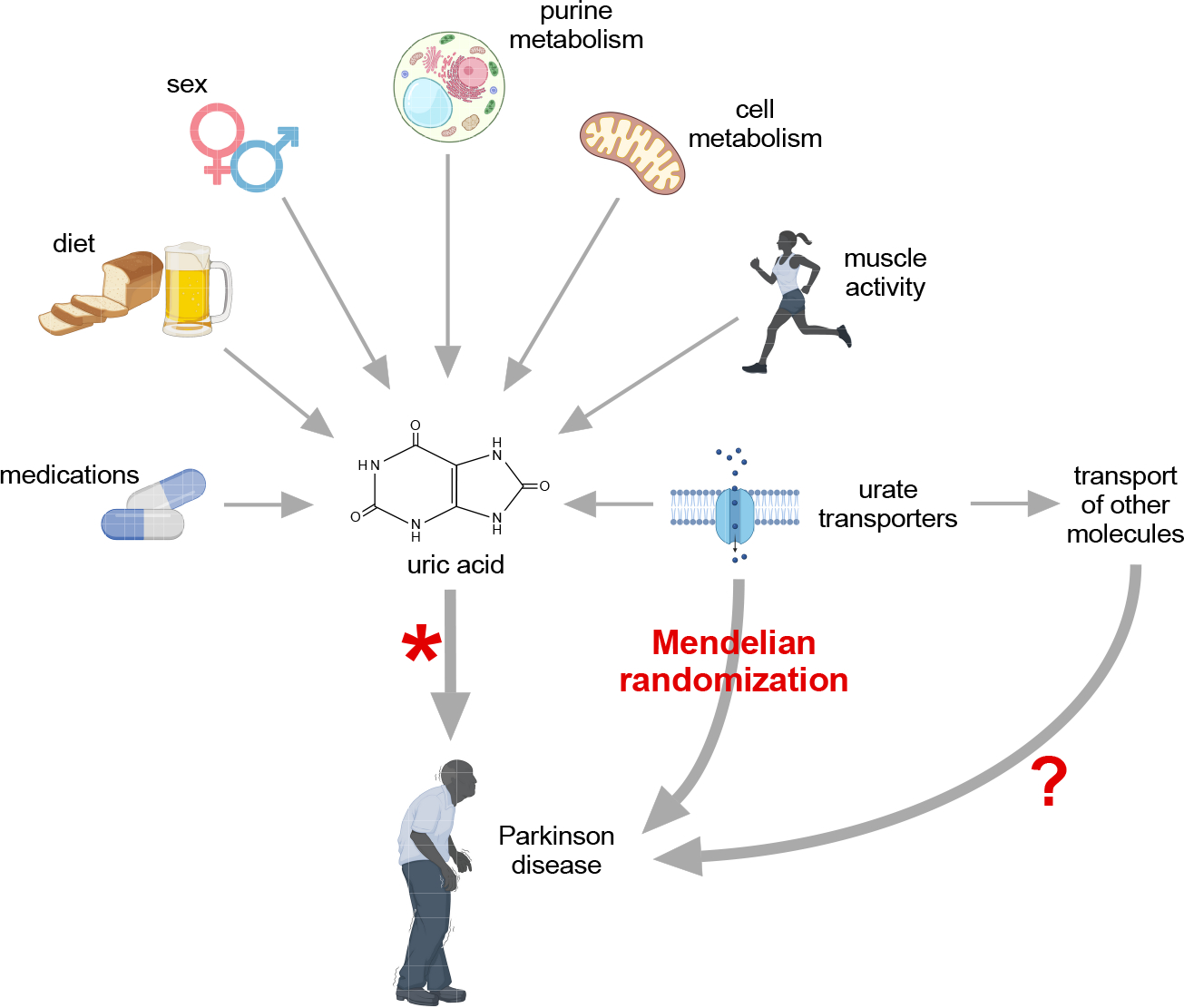
The relevance of Mendelian randomization studies in Parkinson disease. These studies did not find any association between transporters of uric acid and Parkinson disease, questioning the idea that low UA causes PD or contributes to its progression. However, the available studies cannot definitively confirm nor refute these causal associations between uric acid and PD, because they cannot exclude an impact of other possible molecules on PD (pleiotropy) and the impact of these transporters is biologically relatively small relative to other factors that may have a bigger impact on uric acid levels.
