Figure 7. CALMN interaction plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of CCM disease.
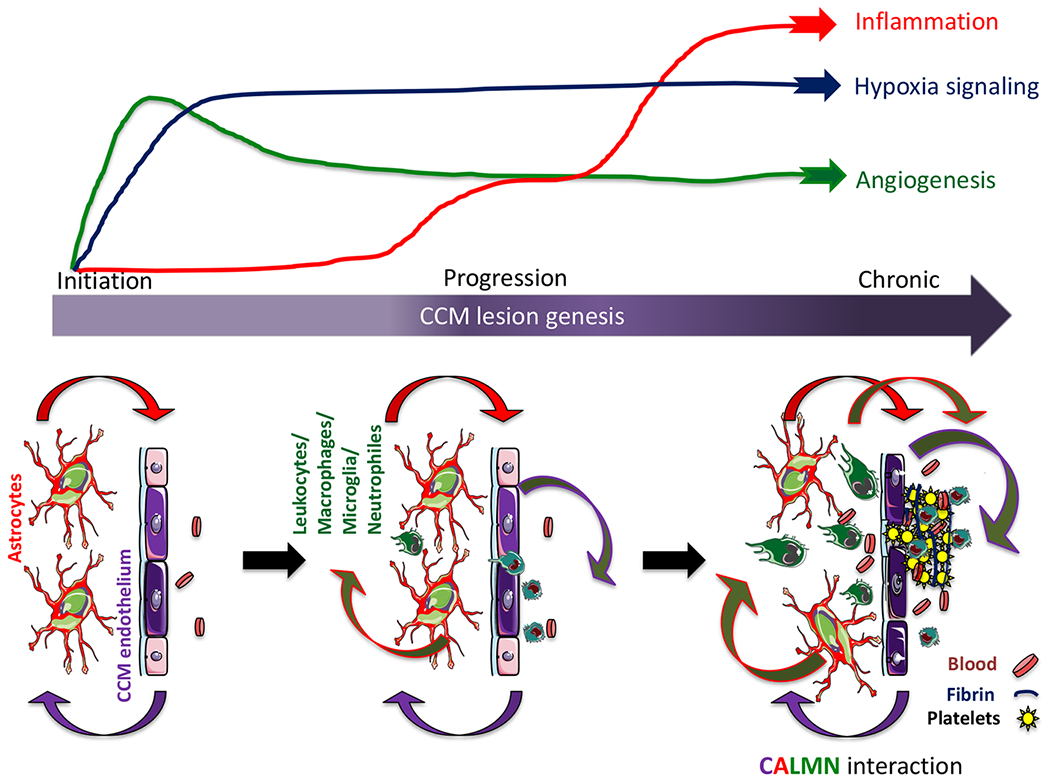
The illustration shows that angiogenesis and hypoxia signaling are essential in CCM lesion formation (initiation)13, while the inflammation pathway initiates in the progression phase and may contribute to mature active CCM lesions, lesion growth, immunothrombosis, and bleedings. Our model proposes that CCM endothelium and astrocytes synergize to recruit inflammatory cells to CCM lesions. Moreover, a reciprocal interaction between CCM endothelium, astrocytes, leukocyte, and macrophage/microglia, neutrophils, that we termed CALMN interaction, is critical for the transition of lesions into aggravating active lesions.
