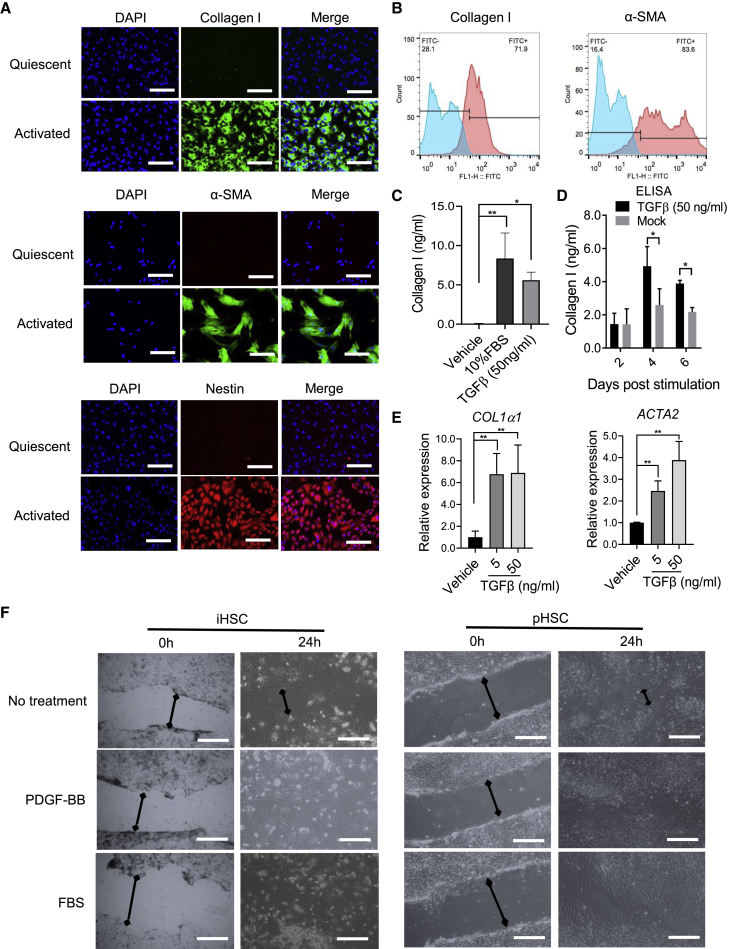
Figure 4.
Activated HSC marker expression increases during activation as shown by functional analysis
The iHSCs were seeded in Matrigel-coated plates and activated by TGF-β (50 ng/mL) or 10% FBS in basal medium for 5 days. The related markers were detected by different assays.
(A) Representative images of collagen I, α-SMA, and nestin comparing quiescent iHSCs and iHSCs activated by TGF-β (50 ng/mL) for 5 days. Scale bars, 100 μm.
(B) Representative histograms of flow cytometric analysis of collagen I and α-SMA from quiescent iHSCs and iHSCs activated by TGF-β (50 ng/mL) for 5 days. Blue color means the isotype control and the red color means the tested markers' expression. See also Figure S1E.
(C) Comparison of collagen I expression between 10% FBS and TGF-β (50 ng/mL) treatment by ELISA; n = 3 in each group.
(D) ELISA of collagen I expression during the TGF-β (50 ng/mL) treatment from 2 to 6 days post activation; n = 3 in each group.
(E) qRT-PCR analysis of COL1α1 and ACTA2 expression during TGF-β treatment (5 and 50 ng/mL) for 5 days; n = 3 in each group.
(F) Representative images of the wound-healing assay, showing the scratch closure of iHSCs after incubation with PDGF-BB (20 ng/mL) or FBS (10%) for 24 h. Scale bars, 200 μm. Data are shown as the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. The double-headed arrows means the distance of wound closure of iHSCs after incubation with PDGF-BB (20 ng/mL) or FBS (10%) for 24 h. Student’s t test was used. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01. See also Figures S2 and S3.