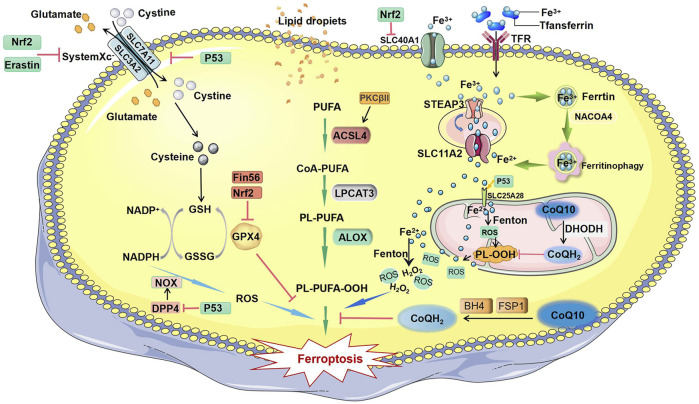
FIGURE 1.
Mechanisms of ferroptosis. The initiation of ferroptosis requires two key signals, lipid peroxidation and accumulation of free iron. The generation of polyunsaturated phospholipids (by ACSL4 and LPCAT3) or PUFA-ePLs (by peroxisomal enzymes) and subsequent activation of ALOX have a major role in promoting lipid peroxidation, which can be inhibited by GPX4 and PKCβII. Extracellular iron enters the cell through TFR and facilitates the Fenton reaction to promote PUFA-PL oxidation. Some free iron stored in ferritin is released by ferritinophagy-mediated ferritin degradation. Iron can promote FSP1-CoQ10-NADPH pathways, and BH4 can block the propagation of phospholipid peroxidation and ferroptosis. Abbreviations: ALOX, lipoxygenase; ACSL4, acyl-CoA synthetase long chain family member 4; BH4, tetrahydrobiopterin; CoA-PUFA, coenzyme A-polyunsaturated fatty acid; CoQ10, coenzyme Q10; CoQH2, ubiquinol; DPP4, dipeptidyl peptidase 4; DHODH, dihydroorotate dehydrogenase; Fin56, ferroptosis inducer 56; FSP1, ferroptosis suppressor protein 1; GPX4, glutathione peroxidase 4; GSH, glutathione; GSSG, oxidized glutathione; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; LPCAT3, lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; NADPH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NADP+, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NACOA4, nuclear receptor coactivator 4; NOX, NADPH oxidase; PKCβII, protein kinase C beta type isoform; PUFA, polyunsaturated fatty acid; PL-PUFA, phospholipid-containing polyunsaturated fatty acid; PL-PUFA-OOH, phospholipid with a peroxidized polyunsaturated fatty acyl tail; P53, protein 53; PL-OOH, phospholipid hydroperoxide; ROS, reactive oxygen species; Slc7A11, solute carrier family 7 member 11; SLC11A2, solute carrier family 11 member 2; SLC25A28, solute carrier family 25 member 28; SLC40A1, solute carrier family 40 member 1; STEAP3, six transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 3; TFR, transferrin receptor.