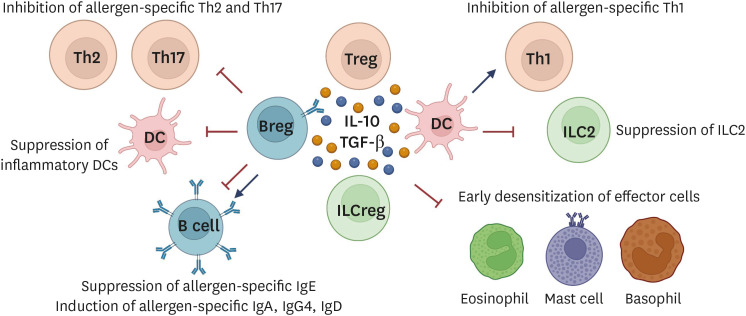
Fig. 1. Mechanisms of immune tolerance induction.
Tregs, Bregs, ILCregs, and tolerogenic DCs produce immunosuppressive cytokines such as IL-10, TGF-β, and IL-35. Tolerogenic DCs express surface molecules that suppress Th2 and Th17 cells as well as inflammatory DCs, and induce allergen-specific Tregs. Tregs suppress early desensitization of effector cells (eosinophils, mast cells, and basophils), effector Th cells (Th1, Th2, and Th17 cells), inflammatory DCs, ILC2, and allergen-sIgE. Through IL-10, TGF-β, and IL-35 cytokines production, allergen-specific IgA, IgG2, IgG4, and IgD antibodies are released and exert IgE-blocking effects. Bregs suppress effector T cells (Th2 and Th17) and induce Treg cell expansion via the release of IL-10, TGF-β, and IL-35 cytokines. Diverse surface molecules on Breg cells including BCR, PDL-1, CD39, CD73, CD80/CD86, CD40, ICOS-L, and AhR are well-expressed and suppress the inflammatory responses. In autoimmune tolerance, Bregs activate iNKT cells with suppressive function. Moreover, Bregs are also the main producer of allergen-specific IgA, IgG2, IgG4, and IgD antibodies that compete with the cross-linking of allergen-sIgE to effector cells. Tregs, regulatory T cells; Bregs, regulatory B cells; ILC, innate lymphoid cell; DC, dendritic cell; IL, interleukin; TGF, transforming growth factor; sIgE, specific IgE; iNKT, Invariant natural killer T; Ig, immunoglobulin.