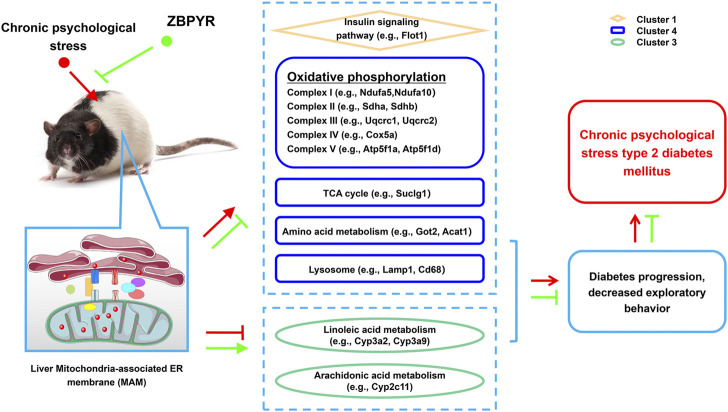
FIGURE 8.
Potential mechanism of T2DM with chronic psychological stress and ZBPYR treatment. Compared with control rats, the proteomics of liver MAM in model rats changed, including insulin signaling pathway, oxidative phosphorylation, TCA cycle, amino acid metabolism, lysosome, linoleic acid metabolism, and arachidonic acid metabolism-related proteins, while ZBPYR treatment caused proteomic changes in liver MAM in ZBPYR rats by regulating the expression of the above proteins. This may underlie the molecular basis of T2DM with chronic psychological stress and the potential therapeutic mechanism of ZBPYR.