Figure 1.
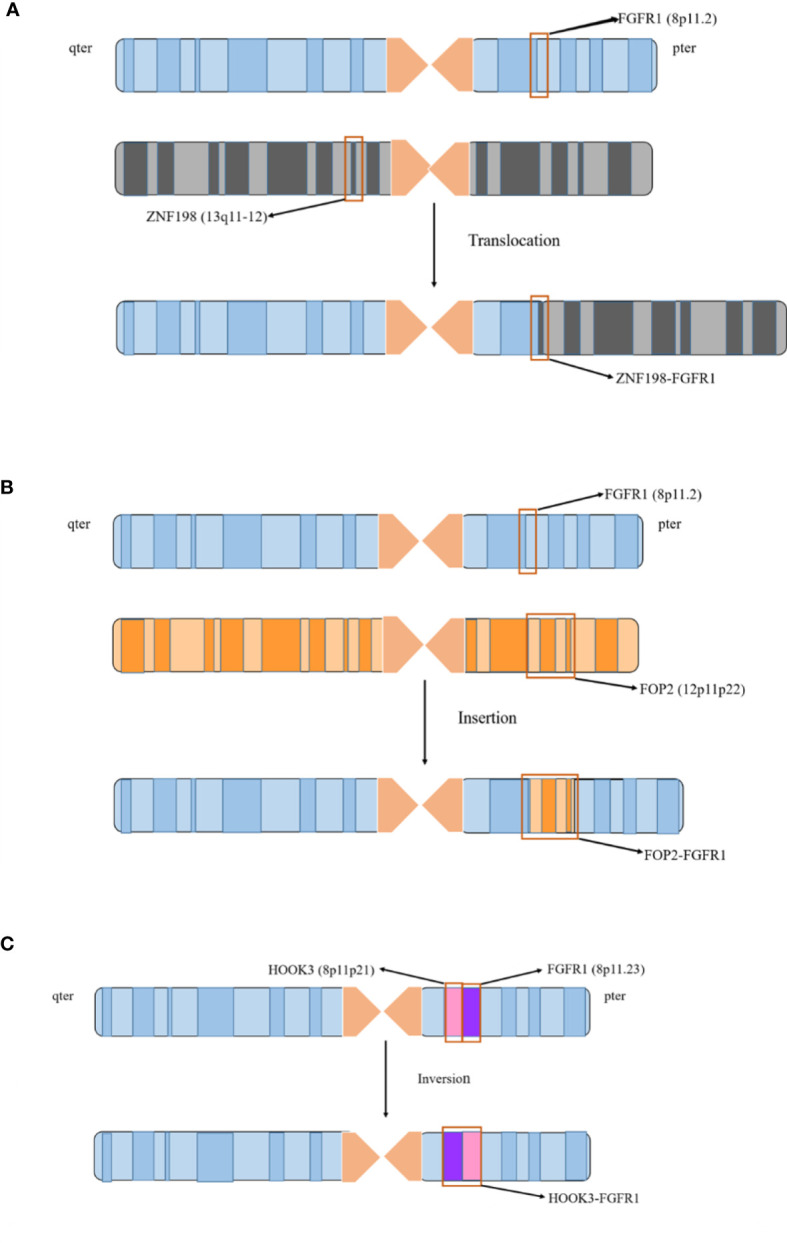
FGFR1 rearrangement involves three chromosomal abnormalities. 17 FGFR1 gene rearrangements existed in EMS, including 15 translocations, 1 insertion, and 1 inversion. (A) The 15 fusion genes are generated from chromosome translocation. It is illustrated by the case of ZNF198-FGFR1 to describe with which chromosome 8 and other chromosomes are formed by translocation. (B) FOP2-FGFR1 is the only rearrangement due to chromosome insertion. The FGFR1 gene on chromosome 8 and the FOP2 gene on the 12p11-p22 are breaking, and the dissociative FOP2 gene is reinserted into the FGFR1 gene fracture to form a fusion. (C) HOOK3-FGFR1 is a recently identified FGFR1 rearrangement in EMS, which is derived from chromosome inversion. The fragment between FGFR1 and HOOK3 genes located on the short arm of chromosome 8 is breaking, and the broken fragment is rotated 180 degrees, resulting in the fusion of HOOK3 and FGFR1.
