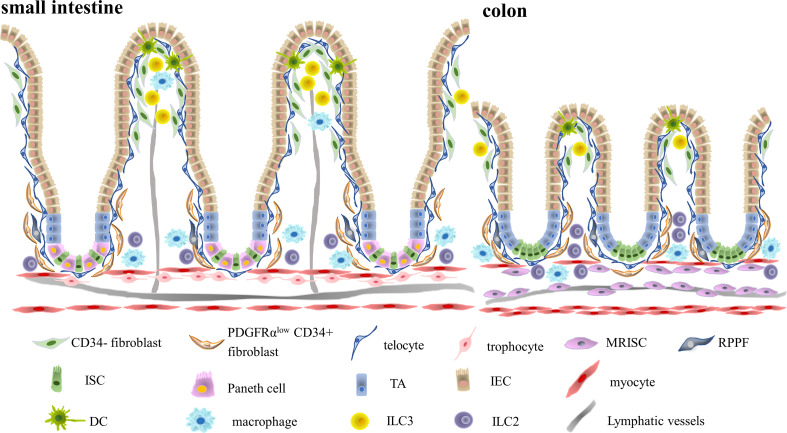
Figure 1.
Two Distinctive Immune Niches Established by Multiple Different Intestinal Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. The intestinal stroma is composed of multiple distinctive intestinal mesenchymal stromal cell subsets including trophocytes, telocytes, fibroblasts and myocytes. Different subsets of intestinal mesenchymal stromal cells occupy different regions. Telocytes are located in the basal membrane right adjacent to the intestinal epithelium, while trophocytes are located in the submucosa. Intestinal fibroblasts are located in the lamina propria. Intestinal immune cells, on the other hand, also occupied different regions of intestinal stroma. CD11c+ dendritic cells mainly resided in the villus tip, while CD206+ macrophages occupied the lamina propria region. Type III innate lymphoid cells are situated in the villus tip and isolated lymphoid follicles, while type II innate lymphocytes are mainly enriched in the submucosa. Therefore, there might be potential interaction between villus tip intestinal stromal cells like fibroblasts or telocytes with CD11c+ dendritic cells in the crypt top and fibroblasts or trophocytes interaction with crypt bottom immune cells like CD206+ macrophages and type II innate lymphocytes. (MRISC, Map3k2-Regulated Intestinal Stromal Cell, RPPF, Rare Peri-cryptal Ptgs2-expressing Fibroblasts, TA, Transit Amplifying Cell, IEC, Intestinal Epithelial Cell, ISC, Intestinal Stem Cell, DC, Dendritic Cell, ILC3, Type III Innate Lymphoid Cell, ILC2, Type II Innate Lymphoid Cell).