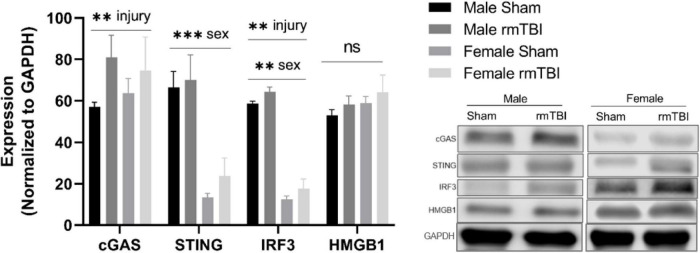
FIGURE 5.
cGAS-STING mediated signaling 1 week post-rmTBI. Western blotting was used to quantify proteins involved in cGAS-STING signaling 1 week after rmTBI. cGAS was significantly increased in rmTBI mice compared to shams (p = 0.005, main effect of injury) with no sex differences. STING was significantly affected by sex (p < 0.0001, main effect of sex), and although trending toward increased expression did not reach statistical significance for effect of injury. Post-hoc analysis revealed STING was significantly increased in sham males compared to both sham and rmTBI females (both p < 0.0001, Tukey HSD), and rmTBI males compared to both sham and rmTBI females (both p < 0.0001, Tukey HSD). IRF3 was significantly increased by injury (p = 0.002, main effect of injury) and affected by sex (p < 0.0001, main effect of sex). Similar to STING, post-hoc analysis indicates that IRF3 expression was significantly higher in sham males compared to both sham females and rmTBI females (p < 0.0001, Tukey HSD). No statistical significant change for HMGB1 was observed. All statistical values are results of two-way ANOVAs with n = 4 per sex-segregated group. Error bars represent standard deviation and indication of statistical analysis is as follows: #p < 0.1, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. ns, not significant.