FIGURE 7.
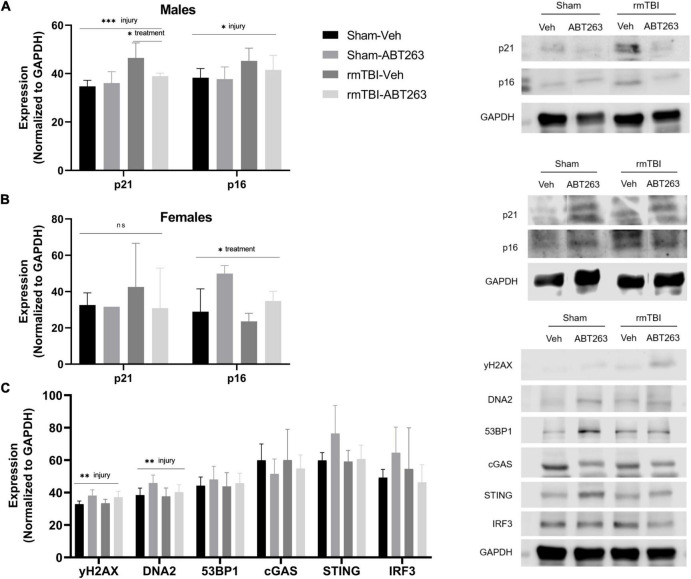
Treatment with senolytic drug ABT263 reduces senescence in males, but not females, following rmTBI. Western blot analysis revealed that ABT263 treatment 1 week after injuries followed by sacrifice 1 week later (total of 2 weeks post-injuries) significantly reduced expression of p21 in male rmTBI mice (A) (p = 0.02, two-way ANOVA), which was significantly increased by injury (p = 0.0003, main effect of injury, two-way ANOVA). p16 was also significantly increased by injury (p = 0.02, main effect of injury, two-way ANOVA) in the males (A) and was only partially reduced by ABT263 treatment, although this did not reach statistical significance. In contrast, females showed no significant differences in p21 protein levels by this timepoint (B). Interestingly, p16 protein levels significantly increased with ABT263 treatment in female mice (p = 0.03, main effect of treatment, two-way ANOVA). ABT-263 treatment did not significantly reduce markers of DNA damage nor cGAS-STING signaling (C) in male mice, indicating the remaining presence of DNA damage and inflammatory signal. Error bars represent standard deviation with n = 4 per group. Statistical significance is marked as *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. ns, not significant.