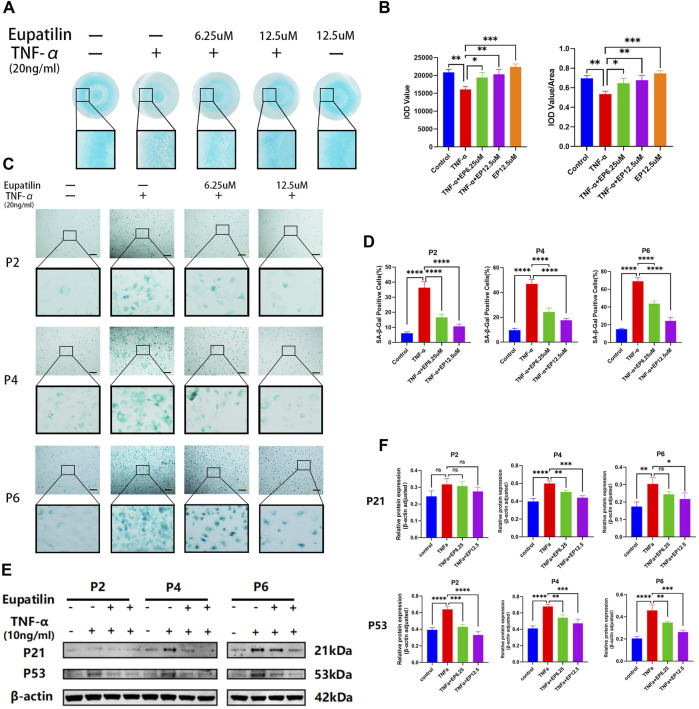
FIGURE 2.
Eupatilin alleviated TNF-α-induced ECM degradation and improved TNF-α-induced senescence of NP cells. (A) In a high-density culture medium, after 9 days of treatment with TNF-α (20 ng/ml) or TNF-α (20 ng/ml) and eupatilin (6.25 μM, 12.5 μM), the results showed that the NP primary cells were stained with Alcian blue. Scale bar, 200 μm. (B) According to the results in (A), the integrated optical density (IOD) value and IOD value/area calculation statistical analysis were performed to evaluate the effect of eupatilin treatment on the ECM of NP primary cells (n = 3). (C) SA-β-Gal staining results showed that the senescence changes of NP primary cells (P2, P4, and P6 generations) were treated by TNF-α (20 ng/ml) or TNF-α (20 ng/ml) and eupatilin (6.25 μM, 12.5 μM) after 3 days. Scale bar, 100 μm. (D) According to the results of SA-β-Gal-positive staining, NP primary cells in (D) were statistically analyzed (n = 3). (E) Western blot analysis showed the effects of eupatilin on p21 and p53 protein levels associated with TNF-α induced senescence of primary NP cells (P2, P4, and P6 generations). (F) According to the expression results of p21 and p53 in (E), data are presented as the mean ± SD. n = 3, compared with the TNF-α-alone group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001; ns: no statistically significant difference.