Figure 6. HDAC inhibition blocks deacetylation from zygote to 2‐cell embryos and leads to premature expression of developmental genes.
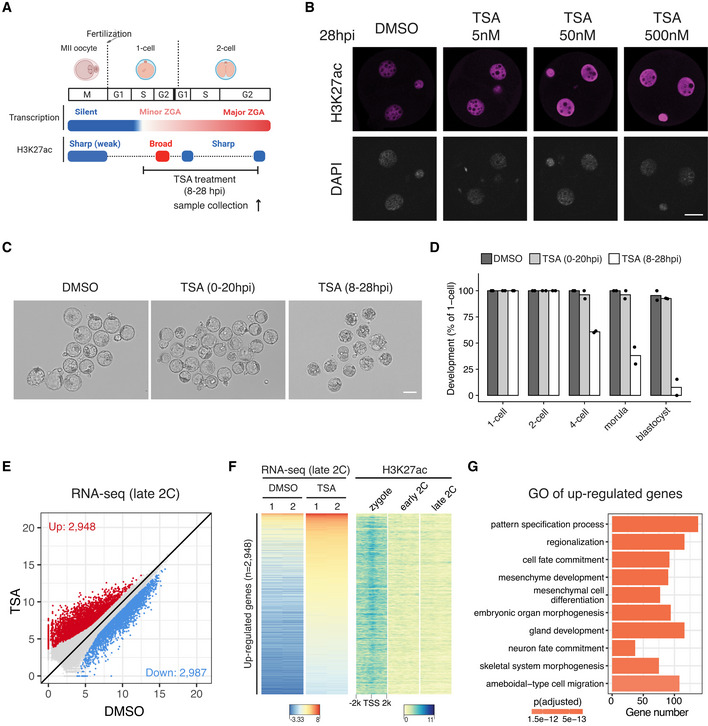
- Schematic illustration of HDAC inhibition from zygotes to late 2‐cell embryos with TSA (Trichostatin A). The cell cycle stages were based on (Abe et al, 2018). The arrow indicates the time point of sample collection for RNA‐seq.
- Immunostaining of H3K27ac in TSA‐treated embryos under different concentrations versus control (DMSO‐treated) at 28 hpi. Scale bar: 20 μm.
- Images of embryos treated with DMSO (control) or TSA at 96 hpi. Scale bar: 80 μm.
- Developmental rate of embryos treated with TSA at different time points (0–20 hpi and 8–28 hpi) versus control.
- Late 2‐cell embryo whole transcriptome comparison between HDAC inhibition (TSA‐treated) and control (DMSO‐treated).
- Heatmap showing the up‐regulated genes after TSA treatment at late 2‐cell stage and the corresponding H3K27ac dynamics at the promoter of these up‐regulated genes.
- Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analysis of the up‐regulated genes after HDAC inhibition.
