Figure 6. CapH and CapP induce CBASS expression in response to DNA damage.
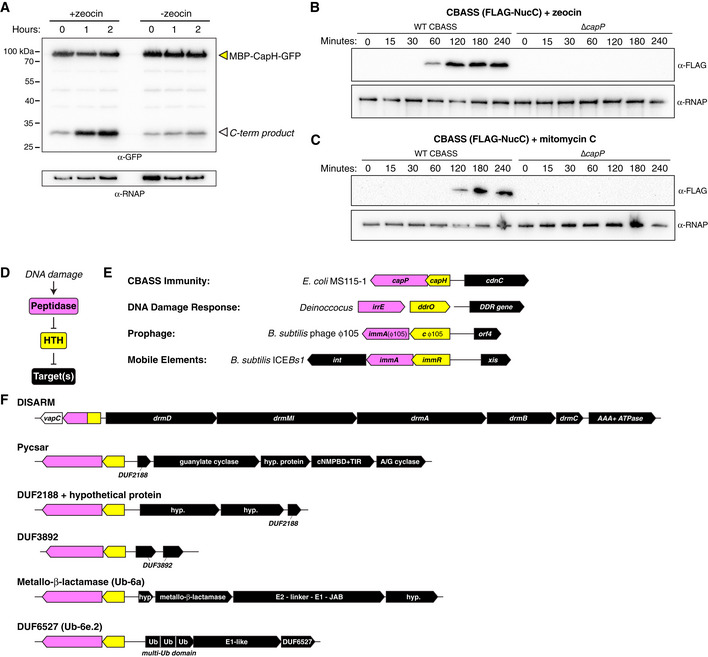
- Anti‐GFP Western blot showing coexpression in E. coli of an MBP‐CapH‐GFP fusion construct with wild‐type CapP after exposure to zeocin (100 μg/ml). Full‐length MBP‐CapH‐GFP is indicated with a yellow arrowhead, and the C‐terminal product of CapP cleavage is indicated with a white arrowhead. α‐RNAP, anti‐RNA polymerase loading control.
- Western blot of the CBASS expression reporter system with FLAG‐NucC, showing FLAG‐NucC expression after exposure to zeocin (100 μg/ml). α‐RNAP, anti‐RNA polymerase loading control.
- Western blot of the CBASS expression reporter system with FLAG‐NucC, showing FLAG‐NucC expression after exposure to mitomycin C (1 μg/ml). α‐RNAP, anti‐RNA polymerase loading control.
- Proposed signaling pathway for DNA damage‐responsive transcriptional control systems in bacteria.
- Diverse systems in bacteria that include an HTH transcriptional repressor (yellow) and a DNA damage‐activated Zn2+ metallopeptidase (pink) that targets the transcriptional repressor for cleavage.
- Known or likely bacterial defense systems associated with CapH (yellow) and CapP (pink)‐like genes. See Materials and Methods for accession numbers for each gene.
Source data are available online for this figure.
