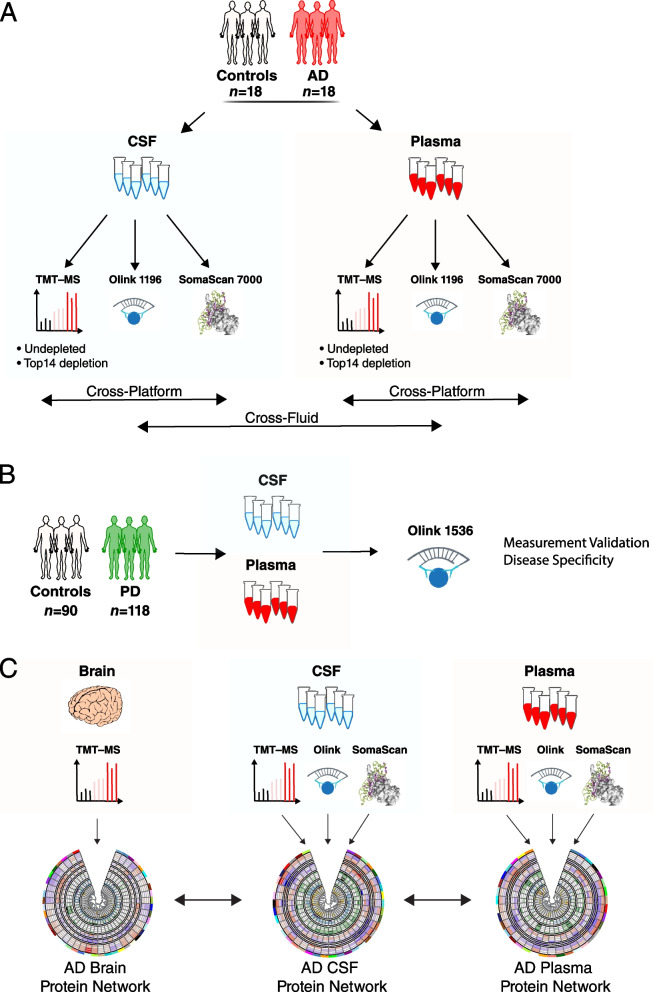
Fig. 1.
Study overview. A–C Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and plasma sampled within subject at or near the same time point from control (n=18) and AD (n=18) subjects was analyzed by three proteomic platforms: untargeted tandem mass tag mass spectrometry (TMT-MS) on both undepleted fluid and fluid depleted of the top 14 most abundant proteins; proximity extension assay (PEA) targeting 1160 unique proteins (Olink 1196); and a modified aptamer-based assay targeting 6596 unique proteins (SomaLogic 7000). B Matched CSF and plasma from 90 control and 118 Parkinson’s disease (PD) subjects were analyzed by PEA targeting 1536 unique proteins (Olink 1536). C Protein co-expression networks for CSF and plasma were separately constructed using the union measurements from all three platforms in each biofluid. Networks were compared across biofluids and with an AD brain network previously described in Johnson et al. [2]