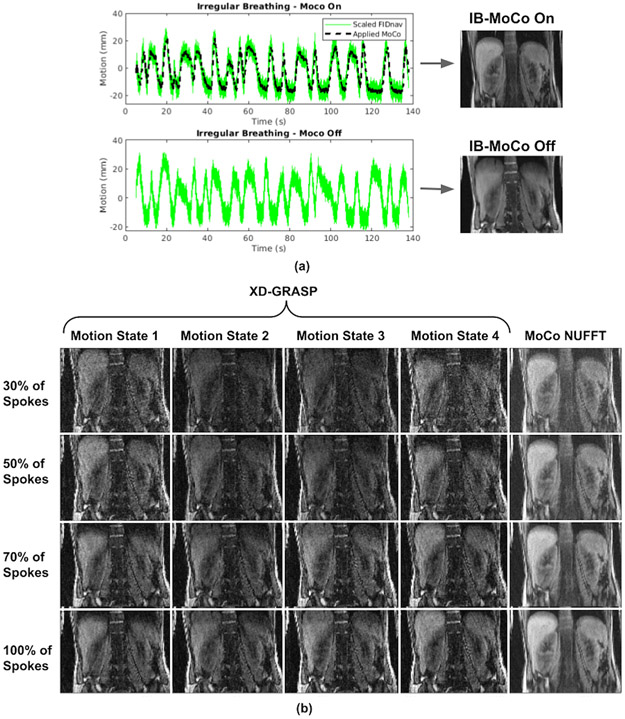
Figure 5.
Results of the irregular breathing experiment. (a) Breathing patterns measured by FIDnav are shown for MoCo On and MoCo Off scans, and applied motion correction for the MoCo scan. (b) NUFFT reconstructions obtained from all 1326 radial spokes for shallow breathing (SB) and irregular breathing (IB) with and without MoCo scans. Despite very irregular and deep breathing patterns, the proposed prospective MoCo technique reduced the motion artifacts. (b) Comparison of proposed method (MoCo NUFFT) with XD-GRASP with regularization along temporal direction for irregular breathing experiment. XD-GRASP method results in noisier images because it uses fewer spokes due to sorting of the spokes into respiratory phases compared to the proposed prospective MoCo technique which effectively uses all spokes. Even when using 30% of all spokes (top row), the proposed technique can generate improved quality images compared to XD-GRASP. Note that the parameters for XD-GRASP had to be hand-tuned and optimized to be able to correctly capture the breathing pattern for the specific volunteer for obtaining the reported results.