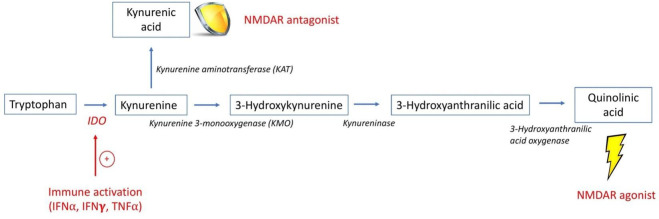
Figure 1.
The kynurenine/tryptophan pathway.1 This is a simplified schematic of the KYN/TRP pathway, highlighting the intermediates and enzymes involved in the production of QA and KA. The enzyme IDO1 is stimulated by inflammatory cytokines, such as IFN, that results in the breakdown of TRP into KYN. KYN may be further metabolised by KMO ultimately to QA, an NMDAR agonist, or by KAT to KA, an NMDAR antagonist. Since the enzyme KMO has higher affinity for KYN than KAT, metabolism proceeds preferentially towards the production of QA in the setting of inflammation.2 26 61 IDO1, indolamine 2, 3-dioxygenase; IFN-α, interferon alpha; IFN-γ, interferon gamma; KA, kynurenic acid; KMO, kynurenine 3-monooxygenase; NMDAR, N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor; QA, quinolinic acid; TNF-α, tumour necrosis factor alpha.