Figure 4.
High affinity GT5 immunogen activates PCT64 precursors at physiological frequencies
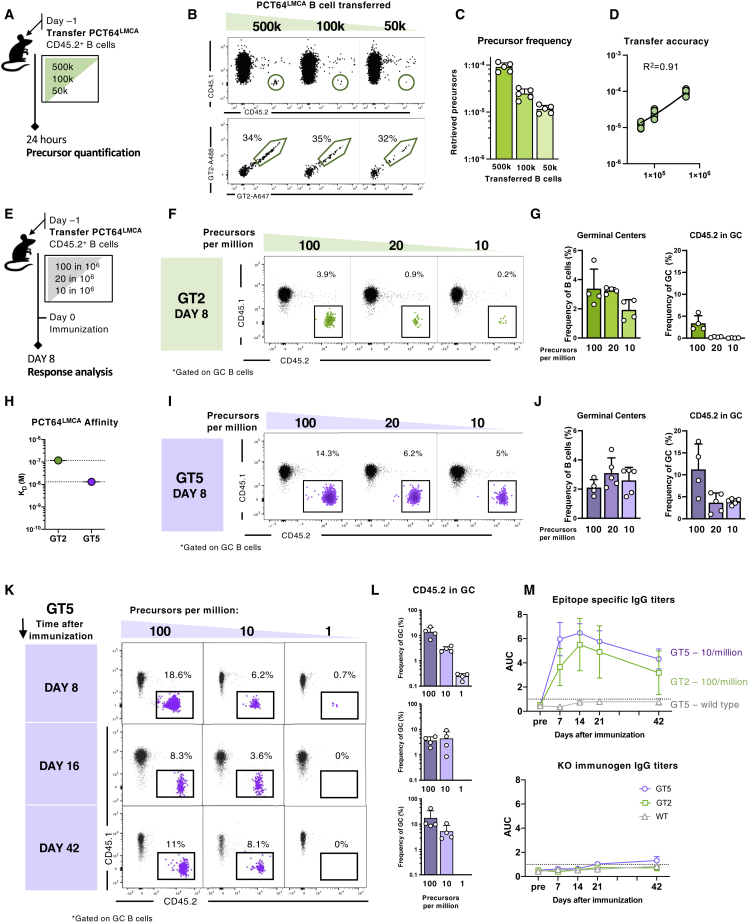
(A) Schematic of adoptive transfer model to calibrate PCT64LMCA B cell frequencies. Experiments were performed in duplicate with one presented; n = 5.
(B) Gating strategy for titration of cell transfer model.
(C) Precursor frequencies (y axis) corresponding to number of B cells transferred (x axis). Bars are mean ± SD.
(D) Analysis of linearity of CD45.2 PCT64LMCA B cells recovered 24 h post transfer.
(E) Schematic of immunizations performed at precursor frequencies of 100, 20, and 10 per 106. Experiments were performed in triplicate with one presented; n = 4.
(F) Representative FACS plots at 8 dpi with GT, showing CD45.2 GC B cell responses at precursor frequency of 100, 20, and 10 per 106 of B cells.
(G) Quantification of GC B cells and CD45.2+ PCT64LMCA cells present in GC at 8 dpi with GT2. Bars are mean ± SD.
(H) SPR of PCT64LMCA for GT2 and GT5 trimers.
(I) Representative FACS plots 8 dpi with GT5, showing CD45.2 GC B cell responses at precursor frequency of 100, 20, and 10 per 106 of B cells.
(J) Quantification of GC cells and CD45.2+ PCT64LMCA cells present in GC at 8 dpi with GT5 at decreasing precursor frequencies (n = 4 and n = 5 for 10:106). Bars are mean ± SD. See also Figures S5F and S5G.
(K) Representative FACS plots at 8, 16, and 42 dpi with GT5, showing CD45.2 GC B cell responses at precursor frequency of 100, 10, and 1 per 106 B cells (n = 4).
(L) Quantification of K. Data are represented as mean ± SD.
(M) ELISA quantification of GT2-/GT5-binding (top) and GT2-/GT5-KO-binding (bottom) serum IgG from PCT64LMCA recipient mice compared to WT C57BL/6J mice (n = 4). AUC was assessed prior to immunization by GT2 or GT5 and at 7, 14, 21, and 42 dpi. Points are mean ± SD.