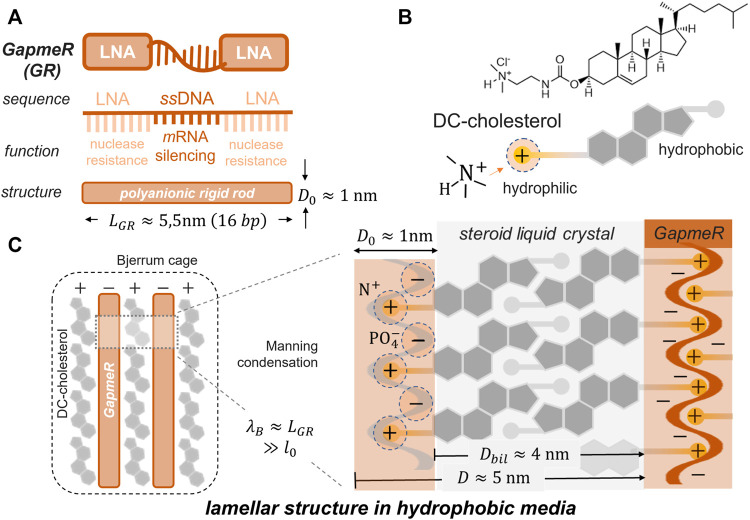
FIGURE 2.
Physicochemical rationale for GapmeR (GR) compaction into lamellar liquid crystal cholesteric phases composed by DC-cholesterol (DChol) under high density Coulombic condensation. (A) Molecular GR construct as a 16 base-pair oligonucleotide; LNA-flanked, single-stranded DNA with the L-PGDS gene-silencing sequence (see Materials for details). Despite electrolytic dissociation of the nucleic acid phosphates ( ), each GR strand appears globally with the electrostatic structure as a rigid rod polyanion; coarse-grained dimensions (16 base-pairs): length ( per bp); diameter. Topological GR parameters (per reactive anionic group (PO4 −); 1bp): specific rod area ; laterally exposed area per anion ; and nominal charge density . (B) Amphiphilic structure of the DC-cholesterol (DChol) molecule, as constituted by the steroidal hydrophobic moiety linked to a hydrophilic counterpart by a tail terminated in the cationic quaternary dimethylammonium head group (Me2N+–), endowed of a large cross-sectional area ( ) and a strong basic characteristic ( ). Approximated molecular dimensions (for DChol chloride; M.W. 537.3 g mol−1; solid density ): specific volume ; Me2N+–head group area ; nominal charge density ; head-to-tail molecular length ; and aspect ratio , predicting a cylinder-like aspect; bilayer former). (C) GR-DChol lipoplexing as promoted at high-compaction inside Bjerrum cages in a low-permittivity dielectric medium (left panel); the Bjerrum length is assumed to have a size comparable to the charged rod length ( ), much larger than the elemental charge size ( ). A lamellar GR-DChol structure promoted by Manning condensation under steroidal mesogenicity is proposed (right panel). Expected topological lipoplex stoichiometry: and , suggesting a chemical formula as two DChol per GR with a bilayer organization for the DChol molecule. Because of the strong acid–base reactivity between GR and DChol, a catanionic 2:1 stoichiometry is assumed under the Coulombic assembly underlying the lamellar bilayer structure (GR: DChol2). Lamellar lipoplex dimensions: The anionic component condensates into parallel GR-monolayers, with a thickness of , which are electrostatically “cemented” by intercalated bilayers made of cationic DChol, with a thickness of . The resulting lamellar spacing expected in Manning-condensing media is expected; therefore, , in agreement with experimental ultrastructural observations (in Figure 4).