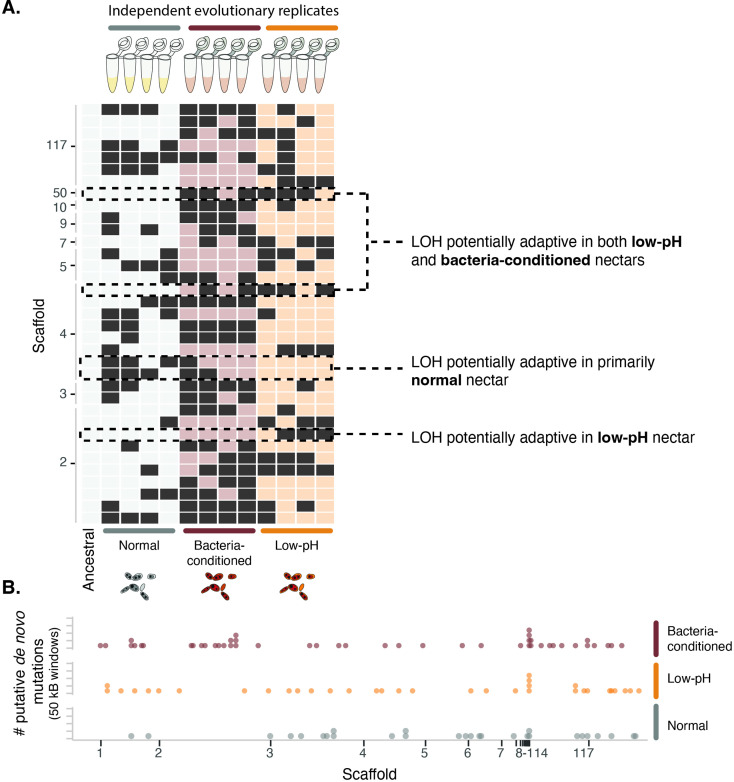
Figure 9. Yeast evolved to synthetic nectar.
(A) Heat map depicting treatment-specific loss of heterozygosity (LOH). Columns represent individual samples (independent evolutionary trajectories) and rows represent single sites with LOH. White or light red/orange boxes indicate sites without LOH, while dark grey boxes represent a site with LOH. Sites selected for the figure exhibited FST >0.3 and permutation-derived p-value <0.1 when comparing the ancestral strain and one of the evolved clones at that site. Boxes with dashed lines are highlighted examples of sites that are potentially adaptive in low-pH nectar, both low-pH and bacteria-conditioned nectar, and normal nectar but not the other two nectar types. (B) Distribution of putative de novo mutations across the genome in 50 kB windows and separated by treatment. Dots represent the sum of putative de novo mutations in a 50 kB window, per treatment (n=146).