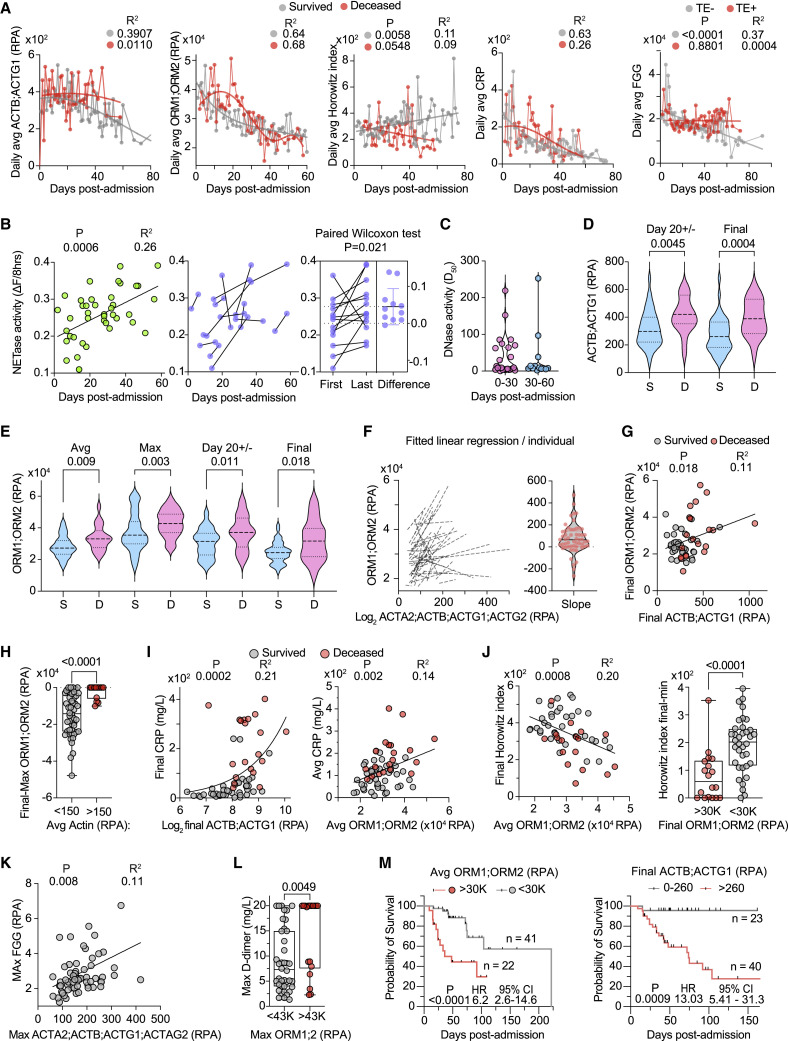
Figure 4.
Relationship between plasma actin, ORM proteins, and infection outcomes
Analysis of 465 samples from 63 CP with maximum WHO-7.
(A) Daily cumulative average relative to time post-admission for actin (ACTB;ACTG1), ORM1;ORM2, HI, and CRP separated by outcome: survivors (gray) or deceased (red). Right: Daily cumulative average FGG in individuals with (TE+ red) or without thromboembolism (TE− gray).
(B) Change in NETase activity over time in 44 CP samples (left). NETase activity in early and late samples connected by a line and the corresponding paired Wilcoxon test for the difference per participant (right).
(C) DNase activity (D50) values obtained from CP samples segregated by 0–30 and 30–60 days post-admission.
(D) Actin (ACTB;ACTG1) abundance in the sample closest to day 20 post-admission (D20+/−) and the final plasma sample obtained from each participant grouped by survival outcome (survived: S, blue; deceased: D, pink).
(E) Average, maximum, D20+/−, and final plasma ORM1;ORM2 per participant grouped by survival outcome.
(F) Fitted linear regression per participant of the correlation obtained from the values for ORM1;ORM2 and actin (ACTA2;ACTB;ACTG1) (left) and violin plot of the corresponding slopes (right).
(G) Correlation between the final values for ORM1;ORM2 and actin (ACTB;ACTG1) per participant who either survived (gray circles) or died (red circles).
(H) Difference between the final and longitudinal maximum ORM1;ORM2 abundance segregated by the corresponding longitudinal average actin values above (red circles) or below (gray circles)150 RPA per participant.
(I) Correlation between the actin and CRP abundance in the final plasma sample collected from each participant (left) or between the longitudinal average ORM1;ORM2 and CRP values (right).
(J) Correlation between the average ORM1;ORM2 and the final HI readings (left). Difference between the final and minimum HI values per participant segregated by whether their final ORM1;ORM2 values were above or below 30,000 RPA (right).
(K) Correlation between longitudinal maximum actin and FGG values.
(L) Longitudinal maximum D-dimer readings in participants with maximum ORM1;ORM2 values above or below 43,000 RPA (right).
(M) Probability of survival in CP clusters according to the longitudinal average values of ORM1;ORM2 (left) or the final actin values (right). Statistics by Mann-Whitney or Kruskal-Wallis test for single comparisons, one-way ANOVA for multiple comparisons, simple linear or non-linear regression for correlations, and Mantel-Cox survival analysis. See also Figure S4.