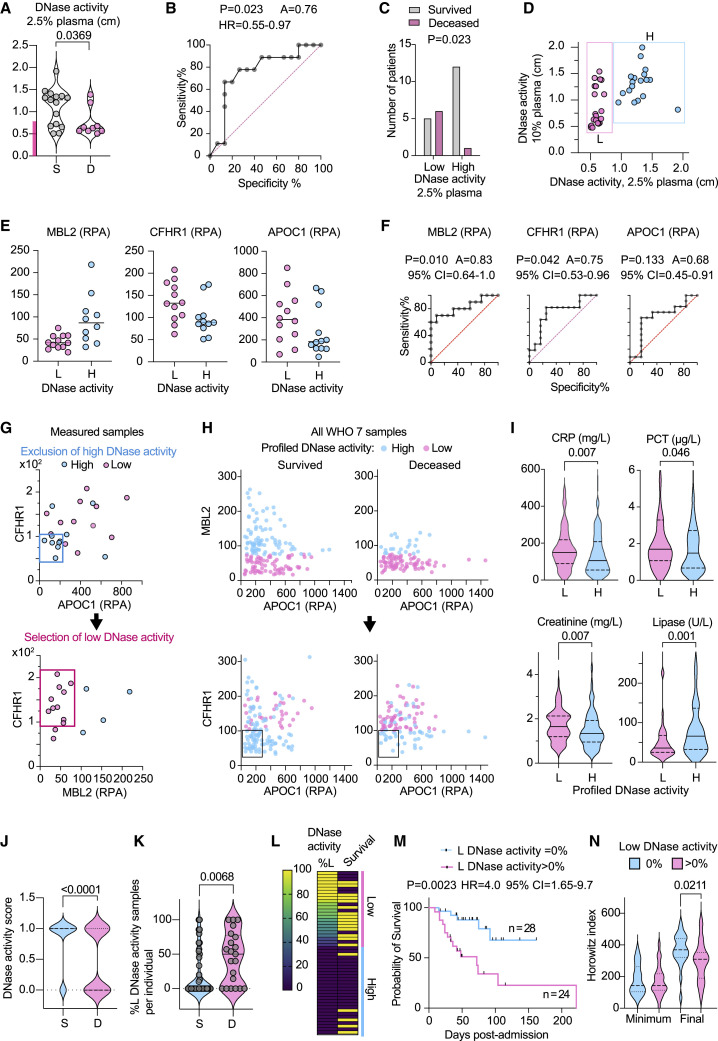
Figure 5.
Low DNase activity is associated with increased COVID-19 mortality
(A) DNase activity in 25 WHO-7 CP samples measured at 2.5% dilution and segregated by survivors (S, gray) or deceased (D, pink). The pink bar in the y-axis indicates low DNase activity.
(B) AUC analysis of CP samples in (A) segregated by low and high DNase activity.
(C) Distribution of survivors and deceased CP in low and high DNase activity groups.
(D) DNase activity measured at 2.5% and 10% CP plasma dilution. The samples clustered as low degraders (L) are shown in pink, and the high degraders (H) are shown in blue.
(E) MBL2, CFHR1, APOC1 abundance in low (L, pink circles) and high (H, blue circles) DNase activity samples.
(F) AUC analysis of MBL2, CFHR1, APOC1 in low (L, pink circles) and high (H, blue circles) DNase activity samples.
(G) Gating strategy for segregation of measured DNase activity samples by proteomic measurements. In the first gating step CHFR1< 100 RPA; APOC1 < 200 RPA gating profiles a high DNase activity group. A second gating step is applied to the remaining samples profiling CHFR1 > 100 RPA; MBL2 < 80 RPA as low DNase activity samples and the excluded are grouped as high DNase activity samples.
(H) Illustration of how gating strategies in (G) apply on 300 WHO-7 CP samples segregated by survival and plotted for MBL2 and APOC1. The top plots illustrate the profiling of low DNase activity using a MBL2 < 80 RPA gate, and the plots below depict the second application of a CHFR1 > 100 RPA; APOC1 < 200 RPA correction filter to identify high DNase activity samples within the low DNase activity group from step one.
(I) CRP, procalcitonin (PCT), creatinine, and lipase values in 300 WHO-7 CP samples segregated by profiled high and low DNase activity.
(J) Distribution of low and high DNase activity assigned by proteomic profiling of 300 WHO-7 samples from 52 participants with maximum WHO-7 in survivors (blue circle) and deceased participants (pink circle).
(K) Fraction of low DNase activity samples per participant segregated by survival outcome.
(L) Heatmap of 52 participants ranked by their content of profiled DNase activity WHO-7 samples. Each row depicts one individual. The first column depicts the percentage of low DNase activity (%L) per participant and the second column depicts the survival outcome where yellow indicates deceased and purple indicates the survivors. Individuals containing only high profiled DNase activity samples (blue bar) or both high and low DNase activity samples (pink bar) are marked on the right.
(M) Probability of survival segregated by whether participants contained low profiled DNase activity samples (pink). The blue curve depicts participants that contained only high profiled DNase activity samples.
(N) Comparison of the longitudinal minimum and final HI values per participant segregated by the whether they contain low profiled DNase activity samples. Statistics by Mann-Whitney or Kruskal-Wallis test for single comparisons, one-way ANOVA for multiple comparisons, simple linear or non-linear regression for correlations, and Mantel-Cox survival analysis.