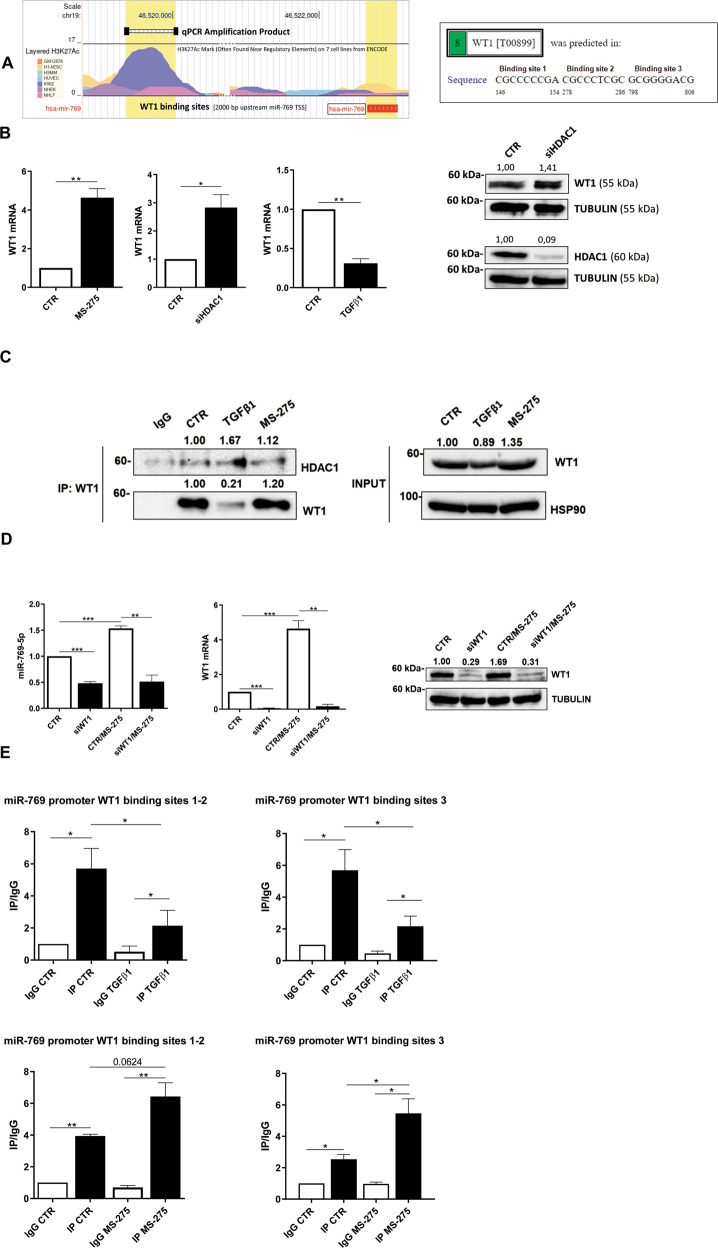
Fig. 5. WT1-mediated induction of miR769-5p is repressed in fibrotic MCs by HDAC1 activity.
A left, predicted WT1 binding site on miR-769-5p promoter by PROMO. Right, study of H3K27 acetylation of miR-769-5p promoter from ENCODE. B Left, RT-PCR showing WT1 mRNA expression upon stimulation with TGFβ1, after HDAC1 genetic silencing, and treatment with MS275 (250 nM for 72 h). Bars represent the mean ± SEM of duplicate determinations in three to four independent experiments. Right, WB showing expression of WT1 (top) and HDAC1 (bottom) upon HDAC1 genetic silencing. Tubulin is used as a loading control. Data are representative of three independent experiments. C left, immunoprecipitation of WT1 showing HDAC1-WT1 interactions upon stimulatin with TGFβ1 and treatment with MS275. A WB of input cell lysates showing WT1 expression and HSP90 as a loading control is shown in the right of the figure. Data are representative of three independent experiments. D RT-PCR showing the expression of miR-769-5p (left) and of WT1 (middle) upon miR-769-5p genetic silencing and treatment with MS-275. Bars represent the mean ± SEM of duplicate determinations in four independent experiments. Right, WB showing the expression of WT1in the same conditions as in D left. Tubulin is used as a loading control. Data are representative of three independent experiments. E qPCR of ChIP assays with anti-WT1 and as control, with normal rabbit IgG on chromatin from MCs from PD patients treated with treated with TGFβ1 for 24 h (top) or with MS-275 for 72 h (bottom) or left untreated (NT) and when indicated. Data show increased binding of WT1 to specific binding sites (1-3) at miR769-5p promoter. Bars represent the mean ± SEM of duplicate determinations in three independent experiments.