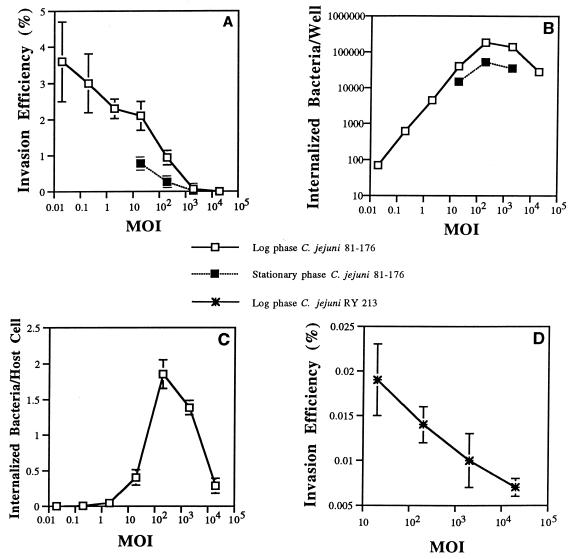
FIG. 1.
Comparative kinetic study showing the effect of varying the starting MOI or phase of bacterial growth on C. jejuni 81-176 or mutant RY213 invasion efficiency (percentage of the starting inoculum internalized at the end of the assay) versus the number of bacteria internalized into INT407 cells. All assays were conducted in triplicate and repeated on separate days at least three times. (A) Effect of varying the starting MOI and phase of bacterial growth on C. jejuni 81-176 invasion efficiency. Invasion assays were conducted, as described in Materials and Methods, by testing a range of starting bacterial concentrations (expressed as MOIs) and using a 2-h invasion period and a 2-h gentamicin kill period prior to enumeration of internalized bacteria. Results are presented as the mean invasion efficiency ± SE. (B) Effect of varying the starting MOI and phase of bacterial growth on total number of bacteria internalized. Invasion assays were conducted as described above. Total number of internalized bacteria per assay well is expressed as CFU per well. Results are presented as the mean CFU per well ± SE. Numbers of CFU per well obtained at MOIs of 200 and 2,000 were significantly greater than numbers of CFU internalized at lower starting MOIs (P < 0.01). (C) Effect of varying the MOI on the resulting number of internalized bacteria averaged per epithelial cell. Invasion assays were conducted as described above. The total number of internalized log-phase C. jejuni 81-176 bacteria is expressed as the average number of bacteria internalized per epithelial cell (obtained by dividing total internalized bacteria by 105 epithelial cells in each well). Results are presented as the mean of the average number of bacteria per epithelial cell ± SE. The resulting averaged numbers of bacteria per epithelial cell at MOIs of 200 or 2,000 were significantly (P < 0.01) greater than numbers obtained at lower starting MOIs. (D) Effect of varying the MOI on the invasion efficiency of log-phase C. jejuni RY213. Invasion assays were conducted as described for panel A, and results are reported as mean invasion efficiency ± SE.