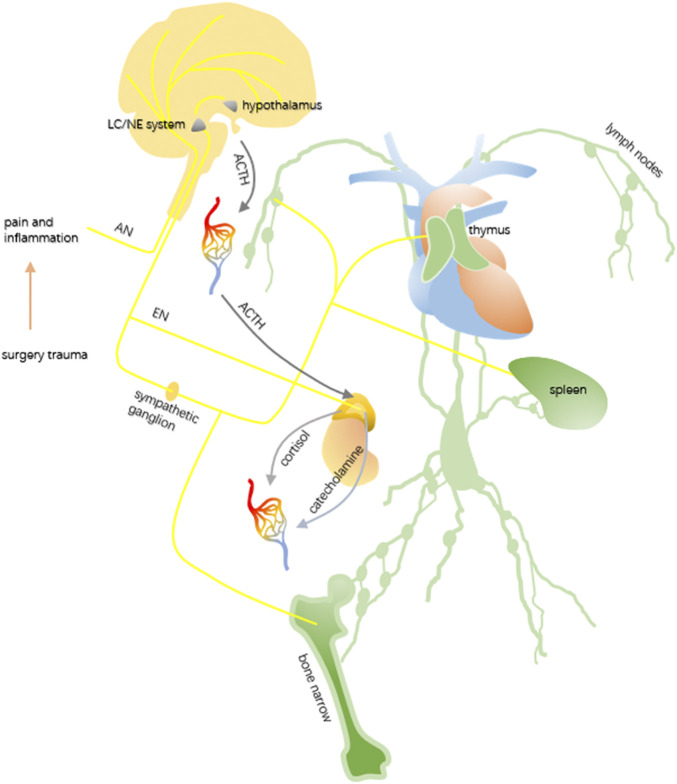
FIGURE 4.
Simplified mechanism of immunosuppression induced by surgery damage. Tissue injury caused by surgery stimulates the afferent neuron (AE). The cerebrum accepts the stimulation, processes the information, and sends them to a special function unit. The locus coeruleus–noradrenergic system (LC/NE system) rapidly transmits the instruction to the immune organs and adrenal medulla through the efferent neuron (EN) and sympathetic nervous system (SNS). Affected by the hypothalamus, the anterior pituitary secretes the adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) to promote the release of cortisol. Both of these contribute to the inhibition of the immune system.