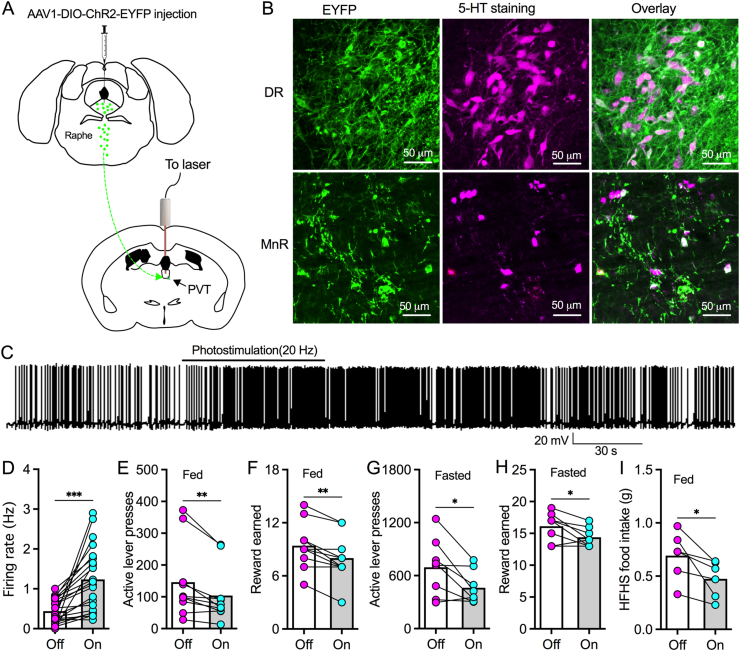
Figure 2.
Photostimulation of raphe-PVT 5-HT projections excites PVT neurons and reduces food motivation. A, A diagram showing AAV1-DIO-ChR2-EYFP was injected into both DR and MnR of Sert-Cre mice. Fiber optics were implanted to target PVT for photostimulation. B, ChR2-EYFP-positive (left) and 5-HT immunoreactive (middle) neurons were found to be colocalized (right) in both DR (above) and MnR (bottom). C, A representative trace showing photostimulation (20 Hz) of raphe-PVT 5-HT axonal terminals excited a PVT neuron from a Sert-Cre mouse with AAV1-DIO-ChR2-EYFP injection into raphe nuclei. D, Bar graph with data plots showing photostimulation (20 Hz) of raphe-PVT 5-HT projections increased firing rate of PVT neurons. ∗∗∗p < 0.001, n = 22 neurons, paired t test. E, Photostimulation of raphe-PVT 5-HT projections reduced active lever presses for HFHS pellets of regularly fed mice during a 45-min PR session. ∗∗p < 0.01, n = 10 mice, paired t test. F, Photostimulation of raphe-PVT 5-HT projections decreased HFHS reward retrieval in regular fed mice during a 45-min PR session. ∗∗p < 0.01, n = 10 mice, paired t test. G, Photostimulation of raphe-PVT 5-HT projections reduced active lever presses for HFHS pellets of 24-h fasting mice during a 45-min PR session. ∗p < 0.05, n = 8 mice, paired t test. H, Photostimulation of raphe-PVT 5-HT projections decreased HFHS reward retrieval in 24-h fasting mice earned during a 45-min PR session. ∗p < 0.05, n = 8 mice, paired t test. I, Photostimulation (20 Hz) of raphe-PVT 5-HT projections decreased HFHS food consumption over 30 min ∗p < 0.05, n = 6 mice, paired t test.