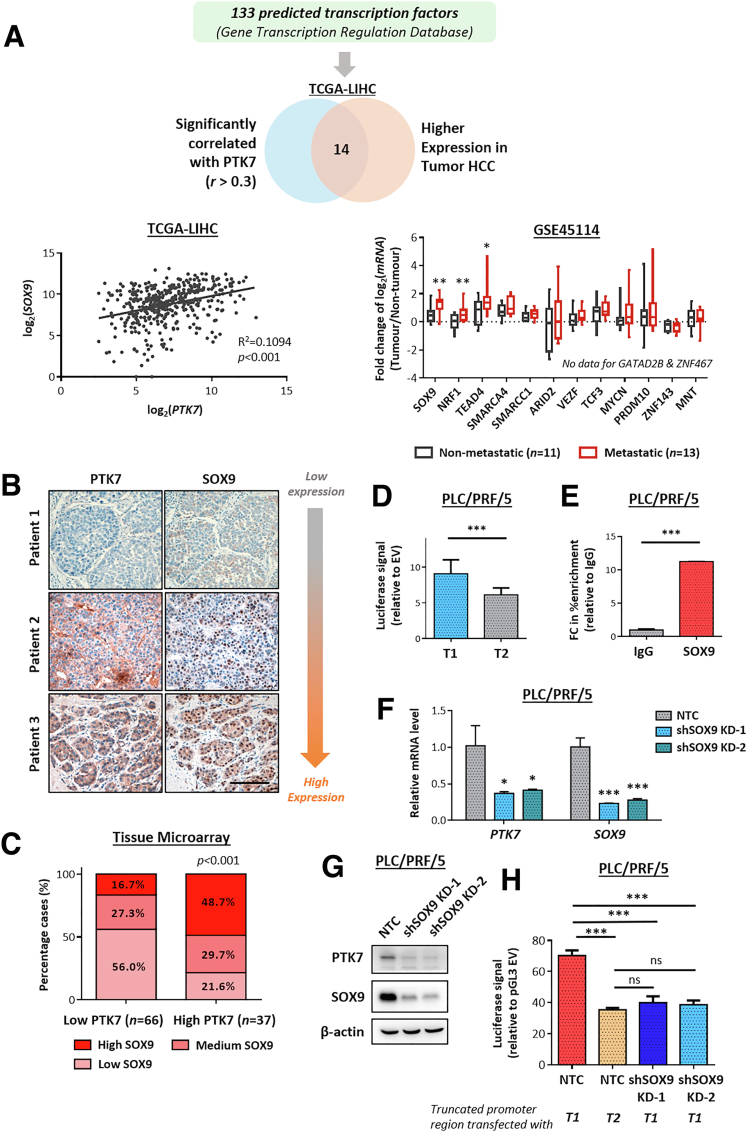
Figure 3.
The expression level and transcriptomic activity of SOX9 are clinically and functionally correlated with PTK7. (A) A total of 133 TFs potentially binding to the promoter region of PTK7, proximal to the transcriptional start site (between -1000 and +1), were compiled from the online Gene Transcription Regulation Database. Fourteen candidate TFs that highly correlated with PTK7 (r > 0.3, determined by Pearson correlation) and were overexpressed in tumor HCC at the messenger RNA (mRNA) level (analyzed using TCGA-LIHC data as a normalized count) were examined further for their specific enrichment in metastatic HCC using GSE45114 data. Only SOX9, nuclear respiratory factor 1 (NRF1), and TEA domain transcription factor (TEAD4) satisfied all of the tested criteria. The correlation of SOX9 and PTK7 expression at the mRNA level is shown for reference. (B) IHC was performed on TMA to investigate the extent of SOX9 nuclear localization in tumor HCC samples in which cases were designated as SOX9 high (>75% nuclei), medium (25%–75% nuclei), or low (<25% nuclei), depending on the amount of tumor cells showing apparent SOX9 nuclear staining. Graded expression of SOX9 was compared with PTK7 in the same TMA. Representative images of IHC are shown. Scale bar: 100 μm. (C) The distribution of cases with various nuclear SOX9 expression in the high-PTK7 and low-PTK7 samples of TMA was compared using the chi-squared test. (D) Two truncated versions of the PTK7 promoter region, one containing the predicted SOX9 binding site (T1) and one without (T2), were expressed in HCC cell lines via transient transfection. The ability of the promoter elements to drive protein expression was quantified using the Dual-Glo luciferase reporter assay and compared using the Student t test. (E) A ChIP assay was performed in HCC cell lines to examine the physical binding of SOX9 to the PTK7 promoter region. Targeted enrichment of the predicted binding sequence was quantified using reverse-transcription quantitative PCR and compared with mouse IgG immunoprecipitation control (IgG). (F) The messenger RNA (mRNA) levels of PTK7 and SOX9 were quantified and validated in HCC cells after successful knockdown of SOX9 by short hairpin RNA (shRNA). (G) Western blot validation of PTK7 suppression after SOX9 depletion by shRNA knockdown. (H) Two truncated PTK7 promoter elements, one harboring the predicted SOX9-binding motif (T1) and the other lacking the same motif (T2), were transfected into SOX9-knockdown (KD) cells and nontarget control (NTC) cells. The resultant luciferase signal induced by the 2 elements in the different cell lines was compared using the Student t test. P values (∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .001).