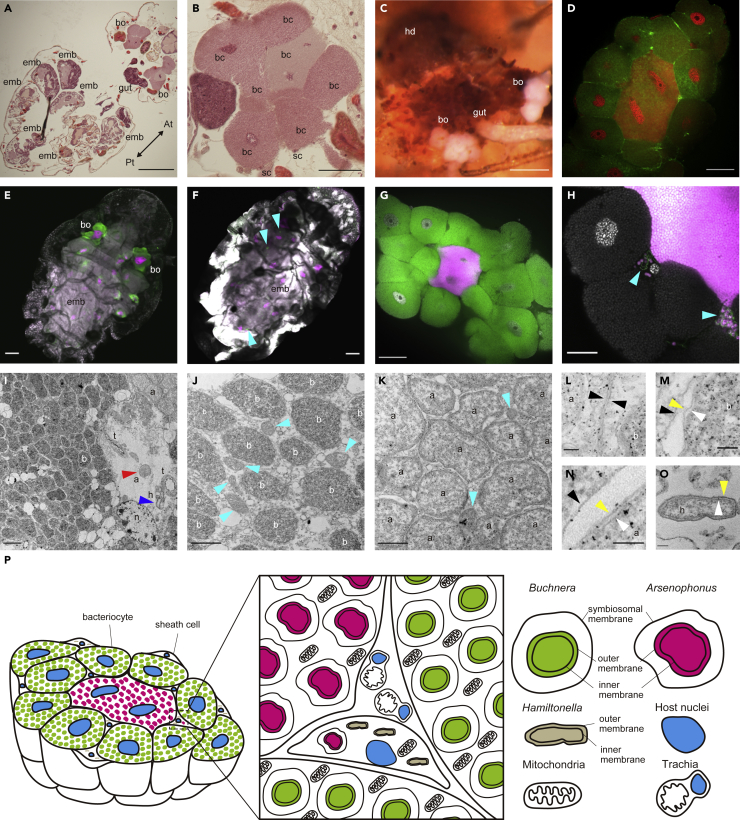
Figure 3.
Localization and morphology of Buchnera and Arsenophonus symbionts
(A and B) Light microscopic images of tissue sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin. The dorsal sections of an adult individual are shown. The whole body (A) and the magnified image of the bacteriome (B).
(C) Light microscopic image of dissected bacteriomes.
(D) Confocal image of the bacteriome structure. Nuclei (red) and F-actin (green) were stained by DAPI and phalloidin.
(E–H) Confocal images of Buchnera, Arsenophonus, and Hamiltonella stained with fluorescent probes specific to each bacterium. Whole bodies of adult individuals (E and F) and dissected bacteriomes (G and H). In (E and G), gray (DAPI), green (Cy5), and magenta (Cy3) signals indicate nuclei, Buchnera, and Arsenophonus, respectively. In (F and H), gray (DAPI), green (Cy5), and magenta (Cy3) signals indicate nuclei, Hamiltonella, and Arsenophonus, respectively. Cyan arrowheads indicate Hamiltonella in (F and H).
(I–O) Electron microscopy of a bacteriome dissected from an adult individual. (I) Low-magnification image of three types of symbionts in the bacteriome. Red and blue arrowheads indicate Arsenophonus and Hamiltonella in the space between bacteriocytes, respectively.
(J and K) Cytoplasm of a bacteriocyte harboring Buchnera (J) and Arsenophonus (K). Cyan arrowheads indicate mitochondria.
(L) Boundary of bacteriocytes harboring Buchnera and bacteriocytes harboring Arsenophonus. Black arrowheads indicate membranes of bacteriocytes.
(M−O) High magnification images of membranes of Buchnera (M), Arsenophonus (N), and Hamiltonella (O) In (M−O), black, yellow, and white arrowheads indicate the symbiosomal membrane, outer membrane, and inner membrane, respectively.
(P) Schematic diagram of the bacteriome morphology. Scale bars show 200 μm in (A and C), 100 μm in (E and F), 50 μm in (B, D, and G), 20 μm in (H), 2 μm in (I), 1 μm in (J and K), and 100 nm in (L–O). a, Arsenophonus; b, Buchnera; bc, bacteriocyte; bo, bacteriome; emb, embryo; h, Hamiltonella; n, host nucleus; sc, sheath cell; t, trachea.