Figure 2. Trade-off between duration/intensity of screening for AF detection of AF, and AF stroke risk.
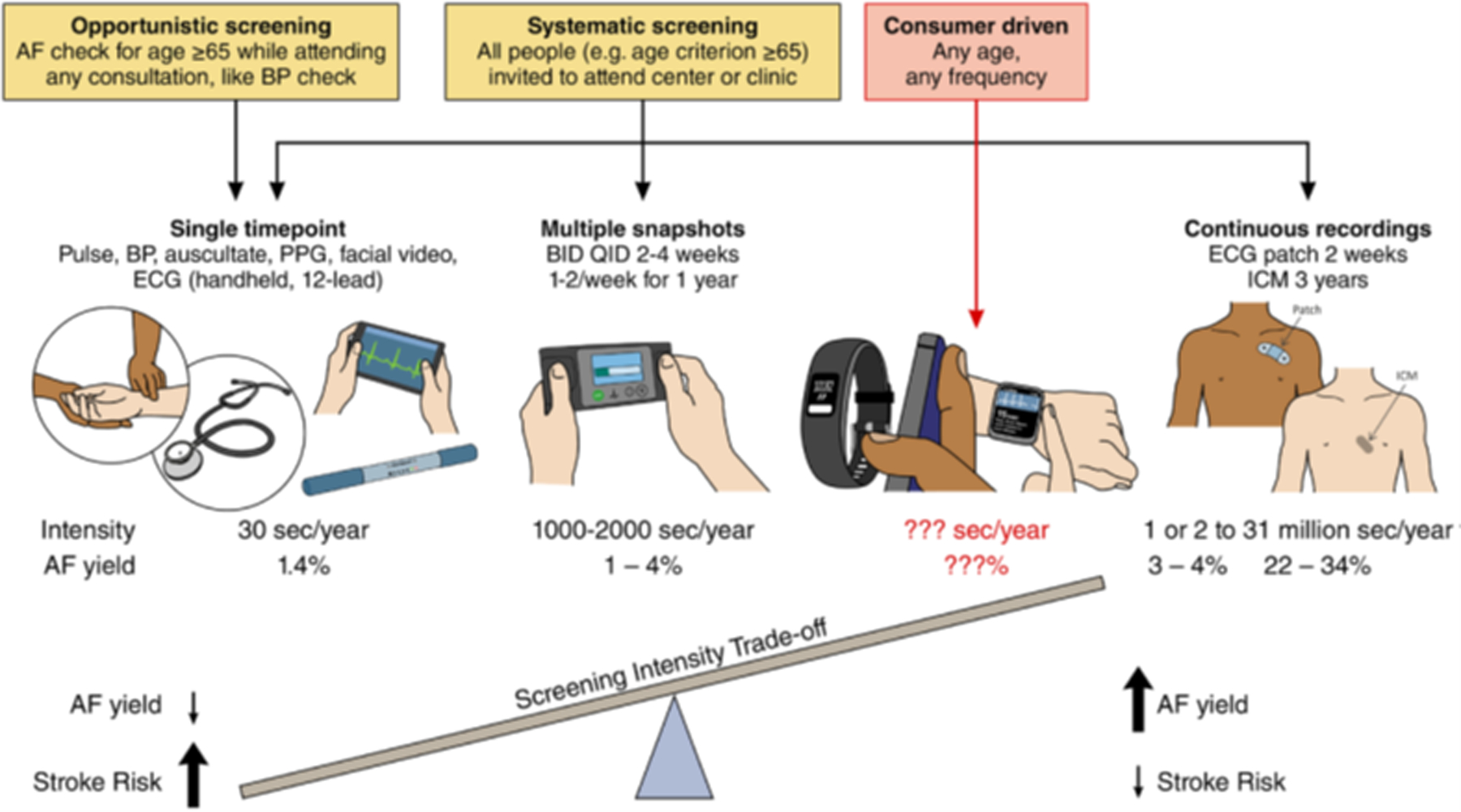
While increased screening intensity increases AF detection rates, it may also identify AF associated with low stroke risk. Nonetheless, the minimum AF burden at which the risk of stroke is sufficient to justify initiation of anticoagulation remains unclear. Therefore, the trade-off between increased detection of low-burden, possibly low-risk AF by continuous monitoring strategies, could be minimized by defining an intermittent monitoring strategy that would diminish the potential for missing individuals with a high burden, which in turn is associated with higher risk of stroke. BID indicates twice daily; BP, blood pressure; ICM, intracardiac monitor; PPG, Photoplethysmogram; and QID, 4 times a day. Modified from Benjamin et al.8
