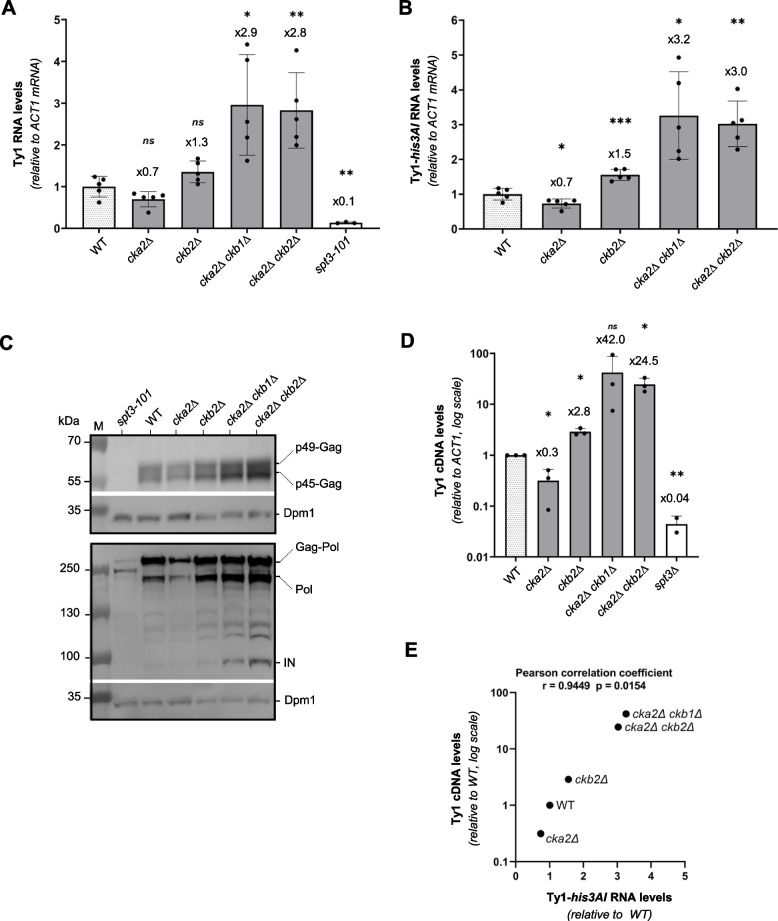
Fig. 4.
Ty1 RNA, protein and cDNA levels increase in the absence of CK2 holoenzyme. A Ty1 RNA levels in WT cells and different mutants of the CK2 complex, as measured by RT-qPCR (mean ± SD, n ≥ 3, relative to WT and normalized to ACT1 mRNAs). B Ty1-his3AI RNA levels in WT cells and different mutants of the CK2 complex as described in panel A. C Whole cell protein extracts of the indicated strains analyzed by Western blot using anti-VLP antibodies revealing p49/p45-Gag proteins, and anti-IN monoclonal antibodies revealing IN, Gag-Pol and Pol intermediates. Dpm1 is a loading control. D Total Ty1 cDNA levels in WT cells and different mutants of the CK2 complex, as measured by qPCR (mean ± SD, n = 3, relative to WT and normalized to ACT1). E Total Ty1 cDNA levels (means ± SD, n = 3, relative to WT, values from panel A) are plotted as a function of total Ty1 RNA levels (mean ± SD, n ≥ 3, relative to WT, values from panel B) in the indicated strains. The Pearson correlation coefficient and associated p-value are indicated. The spt3–101 or spt3Δ null mutants are used as controls for qPCR (Panels A and B), anti-VLP and anti-IN antibodies (Panel D) specificities because Ty1 expression is strongly decreased in these mutants. Unpaired bilateral Student’s t-test: *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001