Figure 1. Overview of study methods and procedures.
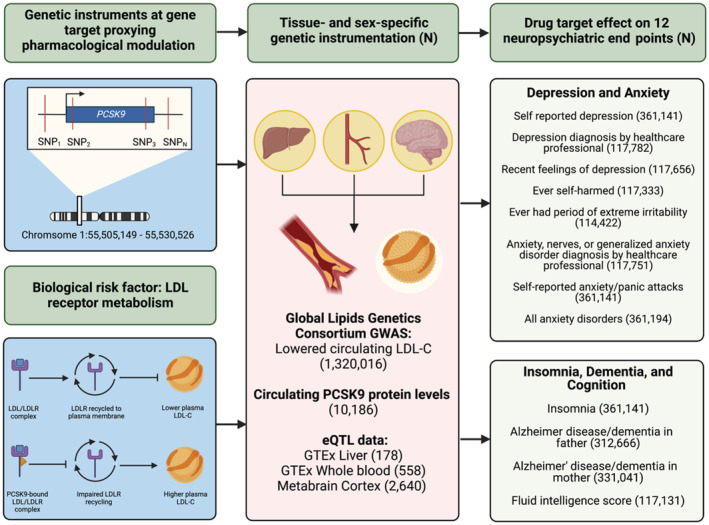
All summary‐level genetic associations were derived from genome‐wide association studies (GWAS) of European ancestry. Additional information regarding the GWAS data (consortium, study cohort, and author information of the GWAS for the exposure and neuropsychiatric outcomes) are located in Table S1. We performed cis‐instrumentation of genetically predisposed PCSK9 (proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9) inhibition in several complementary data sets. First, single‐nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) ±100 kilobases of the PCSK9 gene locus were extracted from the Global Lipids Genetics Consortium (GLGC) 2021 meta‐analysis on circulating low‐density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol (LDL‐C) levels surpassing conventional genome‐wide significance (P<5×10−8). We also proxied PCSK9 inhibition using circulating levels of the PCSK9 protein and tissue‐specific gene expression of PCSK9 in the liver, whole blood, and brain (cortex). These PCSK9 SNPs were then extracted from selected neuropsychiatric end points spanning mood disorders, insomnia, dementia, and cognition from UK Biobank data that combined men and women, as well as male‐only and female‐only GWASs. Finally, we performed drug‐target Mendelian randomization to evaluate the neuropsychiatric impact of genetically predisposed PCSK9 inhibition across men and women (see Methods section). eQTL indicates expression quantitative trait loci; GTEx Genotype‐Tissue Expression; and LDLR, low‐density lipoprotein receptor.
