Figure 4. Sensitivity analyses showing associations between alcohol intake during pregnancy and HDP, gestational hypertension, and preeclampsia.
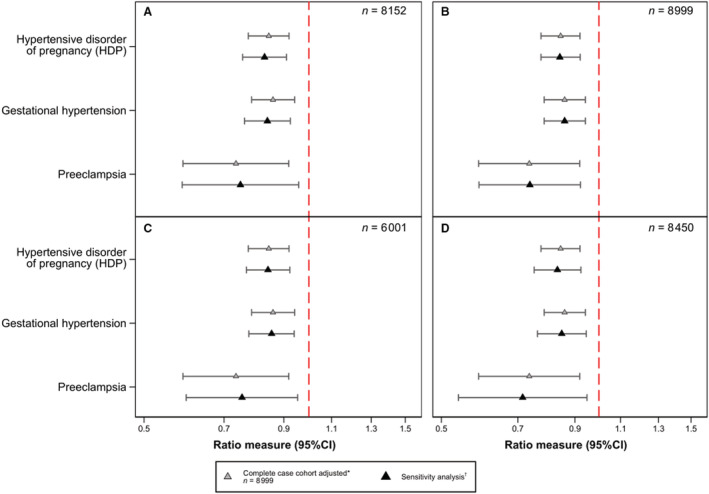
A, Excluding those who had diabetes, kidney disease, arthritis, or multiple pregnancy. B, Using number of cigarettes per day (0, 1–4, 5–9, 10–14, 15–19, 20–29, and 30+). C, Excluding those who reported their alcohol drinking after 20 weeks' gestation. D, Excluding those who reported abstaining from alcohol before their pregnancy. *Adjusted for age, body mass index (BMI), before and during pregnancy smoking (binary), parity, race or ethnicity, educational attainment, and marital status. †Adjusted for age, BMI, before and during pregnancy smoking (binary in model [1] and [3], categorical in model [2]), parity, race or ethnicity, educational attainment, and marital status. The denominator in each analysis is different depending on the criteria of the sensitivity analysis; for example, [1] was performed in those participants from the complete case cohort who had not reported kidney disease or arthritis during pregnancy, did not have diabetes during pregnancy, and had singleton pregnancies (n=8152). HDP indicates hypertensive disorder of pregnancy.
