Figure 6.
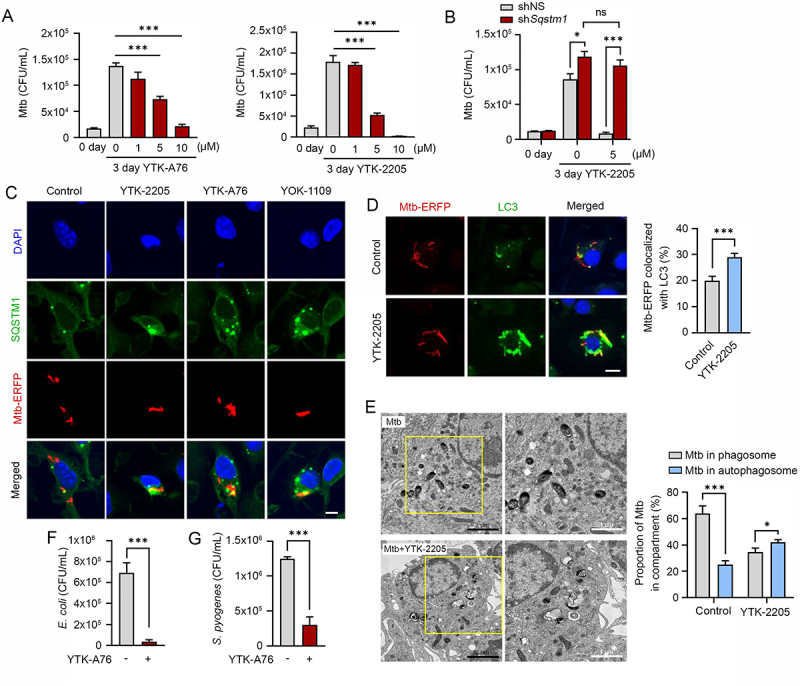
SQSTM1 agonists enhance host innate immunity against Mtb and other pathogens via SQSTM1-mediated xenophagy. (A) Intracellular survival of Mtb assessed in BMDMs treated with YTK-A76 (1, 5, or 10 µM) and YTK-2205 (1, 5, or 10 µM) for 3 days. (B) BMDMs were transduced with lentivirus expressing shNS or shSqstm1, and then treated with YTK-2205 (5 µM) for 3 days. Intracellular survival of Mtb measured by CFU assay. (C) BMDMs were infected with Mtb-ERFP (MOI of 5) for 2 h and then cells were treated with YTK-2205, YTK-A76, or YOK-1109 at 5 μM for 18 h. Colocalization analysis of SQSTM1 (green) and Mtb-ERFP by immunofluorescence analysis. Scale bar: 5 µm. (D) BMDMs were infected with Mtb-ERFP (MOI of 5) and treated with YTK-2205 (5 μM). Colocalization analysis of LC3 (green) and Mtb-ERFP in BMDMs by using immunostaining analysis. Scale bar: 8 µm (left panel). Quantitative graph represents the average percentage of Mtb-ERFP colocalized with LC3 puncta per cells (right panel; n = 11). (E) Representative TEM images of BMDMs treated with YTK-2205 (5 μM) under uninfected or Mtb-infected conditions. Scale bars: 2 µm and 1 µm (left panel). The quantitative graph represents the proportion of Mtb in compartment of autophagosomes or phagosomes in BMDMs (right panel). (F) RAW264.7 cells infected with E. coli for 30 min followed by incubation with SQSTM1 agonist at 10 μM for 6 h. (G) J774A.1 infected with S. pyogenes and treated with SQSTM1 agonist at 10 μM for 6 h. The number of intracellular bacteria was measured by CFU assay.
