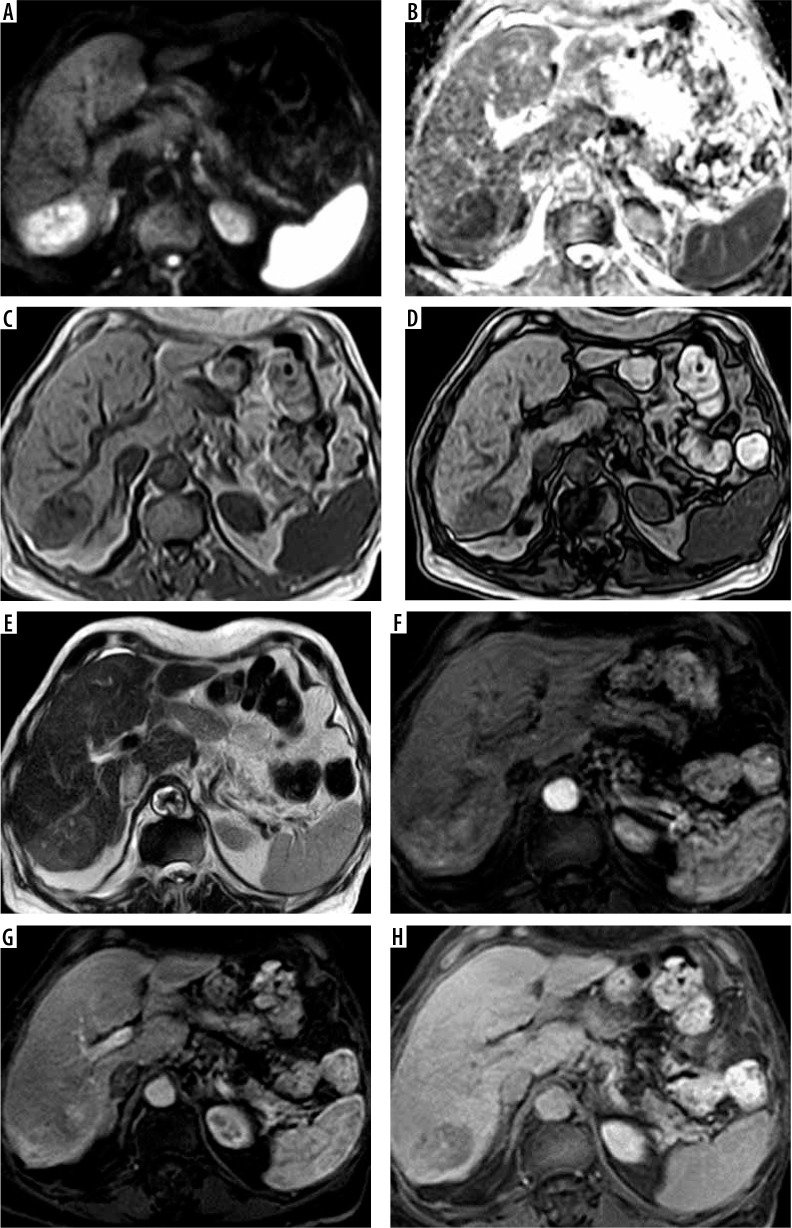
Figure 1.
A-70-year-old male patient with hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, high a-fetoprotein, and liver cirrhosis. Full standard protocol (A, B) axial DWI and ADC showed restricted diffusion in subsegment VII lesion (C, D) axial T1 WI images in phase and out of phase: the lesion elicited a low signal. E) T2WI the lesion elicited a high signal. Dynamic contrast series (F, G, H): arterial phase (F), portovenous phase (G), and delayed phase (H) revealed arterial enhancement of the lesion with portovenous and delayed washout associated with delayed capsular enhancement. The lesion was categorized as LI-RADS-5. Abbreviated 1 protocol: E) T2WI the lesion elicited a high signal. Dynamic contrast series (F, G, H): arterial phase (F), portovenous phase (G), and delayed phase (H) revealed arterial enhancement of the lesion with portovenous and delayed washout associated with delayed capsular enhancement. The lesion was categorized as LI-RADS-5. Abbreviated 2 protocol: A, B) Axial DWI and ADC showed restricted diffusion in subsegment VII lesion. Dynamic contrast series (F, G, H): arterial phase (F), portovenous phase (G), and delayed phase (H) revealed arterial enhancement of the lesion with portovenous and delayed washout associated with delayed capsular enhancement. The lesion was categorized as LI-RADS-5. Abbreviated 3 protocol: C, D) Axial T1 WI images in phase and out of phase: the lesion elicited a low signal. Dynamic contrast series (F, G, H): arterial phase (F), portovenous phase (G), and delayed phase (H) revealed arterial enhancement of the lesion with portovenous and delayed washout associated with delayed capsular enhancement. The lesion was categorized as LI-RADS-5