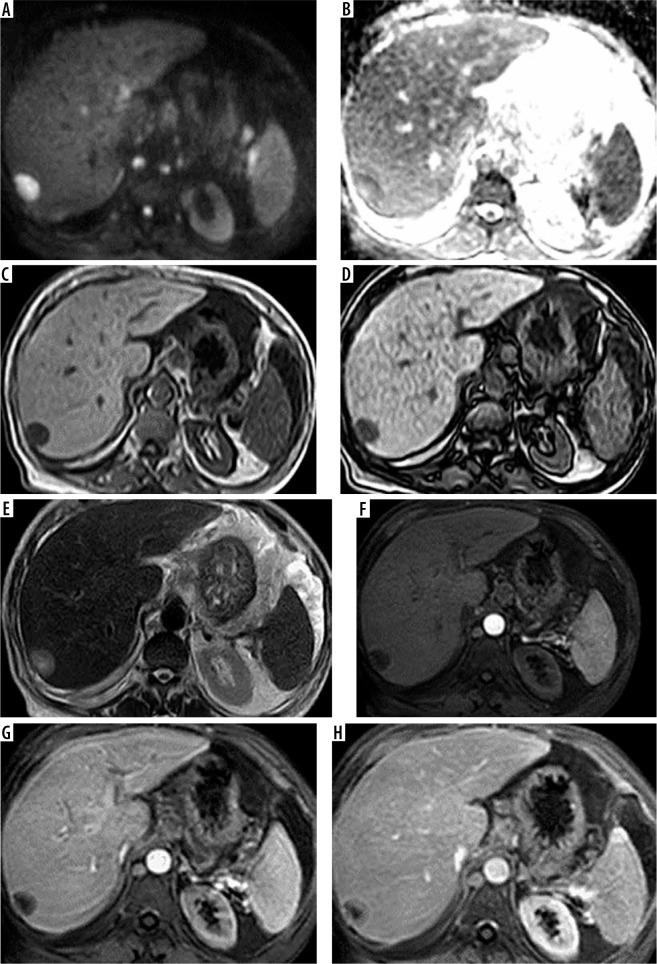
Figure 3.
A 63-year-old female patient with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection presented for screening. Full standard protocol: A, B) Axial DWI and ADC revealed a segment VII lesion with true peripheral diffusion restriction. C, D) Axial T1 WI image in and out of phase: the lesion elicited low signal. E) Axial T2WI image: the lesion elicited a high signal. Dynamic contrast enhancement (F, G, H): arterial phase image (F), portovenous phase (G), and delayed phase (H) revealed arterial enhancement “target sign” with no portovenous or delayed washout. The lesion was categorized as LI-RADS-M. Abbreviated 1: (E) Axial T2WI image: the lesion elicited a high signal. Dynamic contrast enhancement (F, G, H): arterial phase image (F), portovenous phase (G), and delayed phase (H) revealed arterial enhancement “target sign” with no portovenous or delayed washout. The lesion was categorized as LI-RADS-M. Abbreviated 2: (A, B) Revealed a segment VII lesion with true peripheral diffusion restriction. Dynamic contrast enhancement (F, G, H): arterial phase image (F), portovenous phase (G), and delayed phase (H) revealed arterial enhancement “target sign” with no portovenous or delayed washout. The lesion was categorized as LI-RADS. Abbreviated 3: (C, D) Axial T1 WI image in and out of phase: the lesion elicited a low signal. Dynamic contrast enhancement (F, G, H): arterial phase image (F), portovenous phase (G), and delayed phase (H): revealed arterial enhancement “target sign” with no portovenous or delayed washout. The lesion was categorized as LI-RADS-M