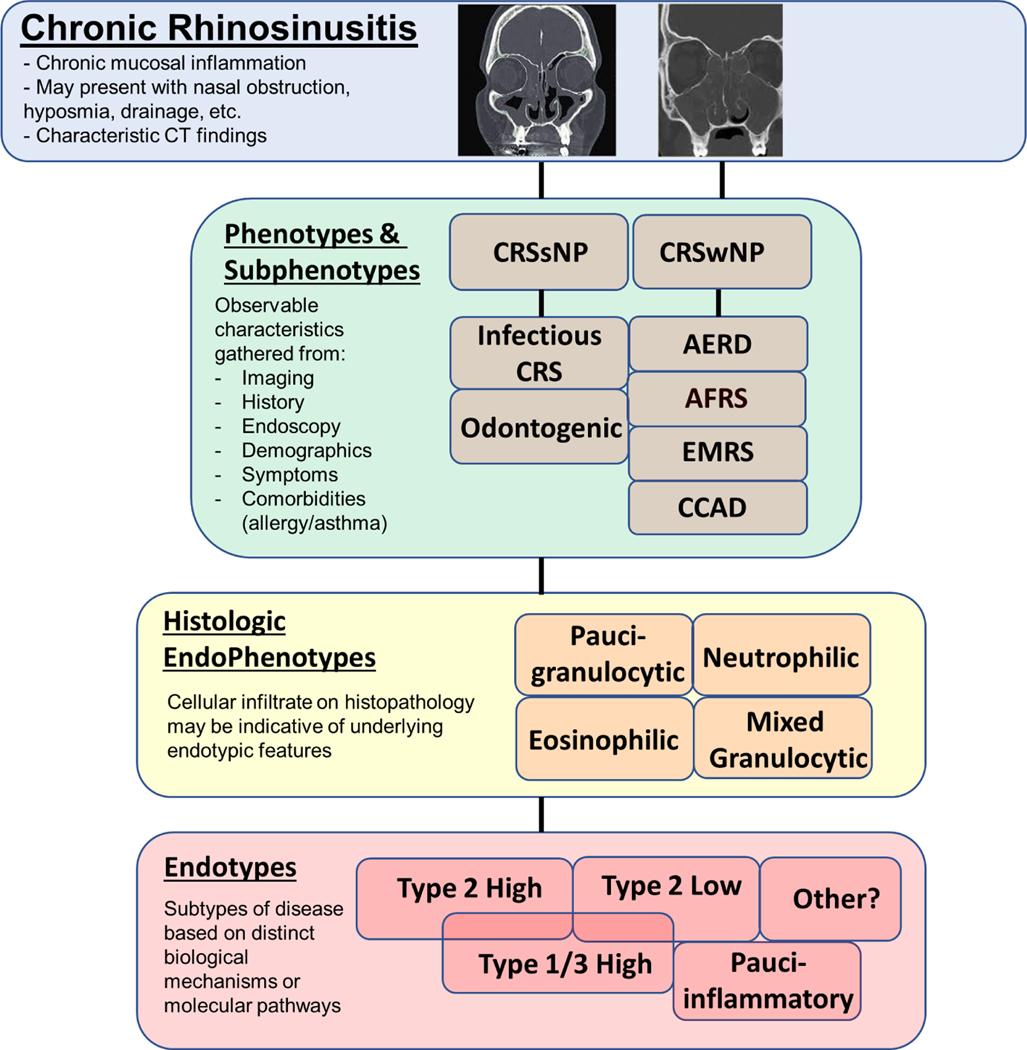
Figure 1. Chronic Rhinosinusitis (CRS) Phenotypes and Endotypes.
CRS is a clinical syndrome characterized by chronic sinonasal mucosal inflammation, variable symptom presentation, and characteristic CT findings. Disease heterogeneity is evidenced by contrasting CT images in CRS patients with nasal polyps (left), without nasal polyps (middle) and AFRS (right). CRS patients can be grouped into phenotypes and subphenotypes based on observable characteristic features or endotypes based on distinct biological mechanisms or molecular pathways. Endotypic features can sometimes be inferred by tissue histology or type of cellular infiltrate. Abbreviations: AERD, aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease; AFRS, allergic fungal rhinosinusitis; CCAD, central compartment atopic disease; CRSsNP, chronic rhinosinusitis without nasal polyps; CRSwNP, chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps; EMRS, eosinophilic mucin rhinosinusitis.