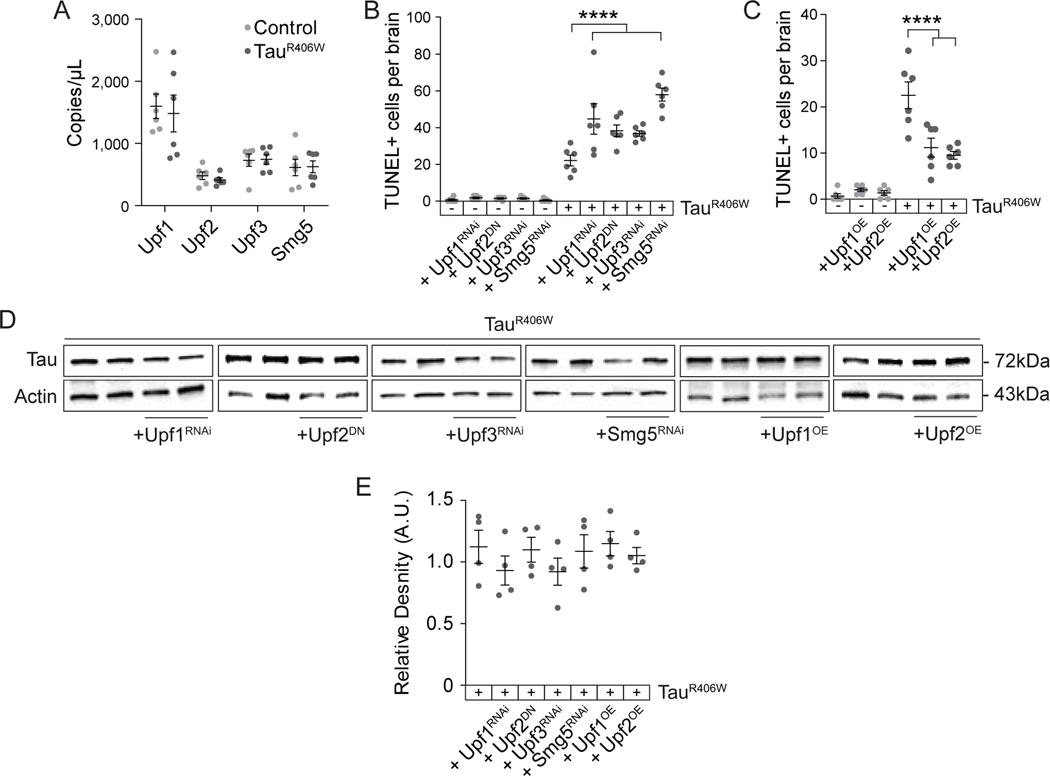
Figure 2 |. Genetic manipulation of NMD modifies tauR406W-induced neurodegeneration in Drosophila.
A) Transcripts levels of Upf1, Upf2, Upf3, and Smg5 are unchanged in control versus tauR406W Drosophila head lysates based on dPCR. B) RNAi-mediated reduction of Upf1, Upf3, and Smg5, and overexpression of Upf2 harboring a dominant-negative mutation significantly enhance tauR406W-induced neuronal death based on TUNEL staining in Drosophila brains. C) Panneuronal overexpression of wild-type Upf1 or Upf2 significantly suppress tauR406W-induced neuronal death based on TUNEL staining in Drosophila brains. D) Genetic manipulation of NMD core factors does not change total protein levels of transgenic tauR406W based on western blotting. E) Quantification of (D), total levels of tau protein normalized to actin. n=4–6 biological replicates per genotype. All assays were performed at day ten of adulthood. ****p<0.0001, one-way ANOVA. Error bars=SEM. Full genotypes are included in Supplemental Table 1.