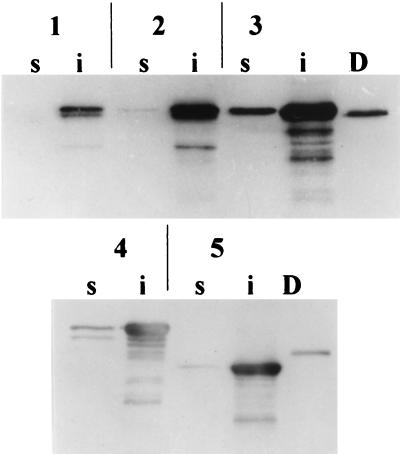
FIG. 2.
Western immunoblot analysis of soluble (s) and insoluble (i) fractions from CVD 908-htrA-expressing CRM197 or its derivatives FC-DTA197 and eDTB197. Membranes were probed with anti-DT antibodies. Lanes D, DT (5 pg); lane 1, pNO1; lane 2, pNO2; lane 3, pNO3; lane 4, pNO7; lane 5, pNO8. E. coli DH5α carrying recombinant plasmids was grown with Luria broth base (LB) medium (Gibco BRL) supplemented with 50 μg of carbenicillin (Sigma, St. Louis, Mo.)/ml. For expression studies, S. typhi CVD 908-htrA was streaked from frozen stocks onto LB agar supplemented with 0.0001% (wt/vol) 2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid (DHB; Sigma) and 50 μg of carbenicillin/ml where appropriate. Isolated colonies were then inoculated into LB broth containing DHB and carbenicillin and incubated overnight at 37°C, 250 rpm. For expression under aerobic conditions, late-logarithmic or stationary-phase cultures were diluted 1:100 into fresh LB broth and again incubated overnight at 37°C, 250 rpm; for anaerobic induction experiments, Oxyrase solution (Oxyrase, Inc., Mansfield, Ohio) was added to identical LB broth cultures and incubated static at 37°C overnight. Selected CVD 908-htrA strains expressing significant levels of CRM197-derived proteins were grown as previously described (7) for immunization of mice. The 150-ml cultures were grown to an optical density at 600 nm, ∼1.0 were centrifuged, and bacterial pellets were resuspended in 3.5 ml of ice-cold sonication buffer (phosphate-buffered saline containing 100 mM KCl, 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, 0.1% Tween 20, and 20 mM β-mercaptoethanol) for solubility studies. Bacterial suspensions were disrupted by sonication for 5 cycles of 20 s on ice by using a model 550 sonic dismembrator (Fisher Scientific, Pittsburgh, Pa.) with a microtip and a power level of 5. Sonicates were centrifuged at 15,000 rpm for 30 min at 4°C, and supernatants representing the soluble fraction were removed; cell pellets were reconstituted with 3.5 ml of sonication buffer to represent the insoluble fraction. Proteins were then heat denatured after equal volumes of sample and lysis buffer were mixed, and proteins from 5 μl of each denatured sample were then separated by SDS-PAGE with 10% polyacrylamide gels. Separated proteins were detected either by staining with BLUPRINT Fast-PAGE Stain (Gibco BRL) or by being transferred to Immun-Lite blotting membrane (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, Calif.) for Western immunoblot analysis. CRM197-derived proteins were detected by using polyclonal goat anti-DT serum (Biogenesis, Sandown, N.H.), and fragment C fusions were confirmed by using monoclonal mouse anti-fragment C antibodies (Boehringer Mannheim, Indianapolis, Ind.). Membranes were then incubated with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated rabbit anti-goat (Sigma) or peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (Gibco BRL) as appropriate. Immunoblots were developed by chemiluminescence with an ECL Western blotting kit (Amersham Life Science Inc., Arlington Heights, Ill.), and signals were detected with X-OMAT XAR-5 film (Eastman Kodak Company, Rochester, N.Y.).