Figure 2. CIC binds and regulates YAP1 expression through non-consensus GGAAGGAA DNA motifs.
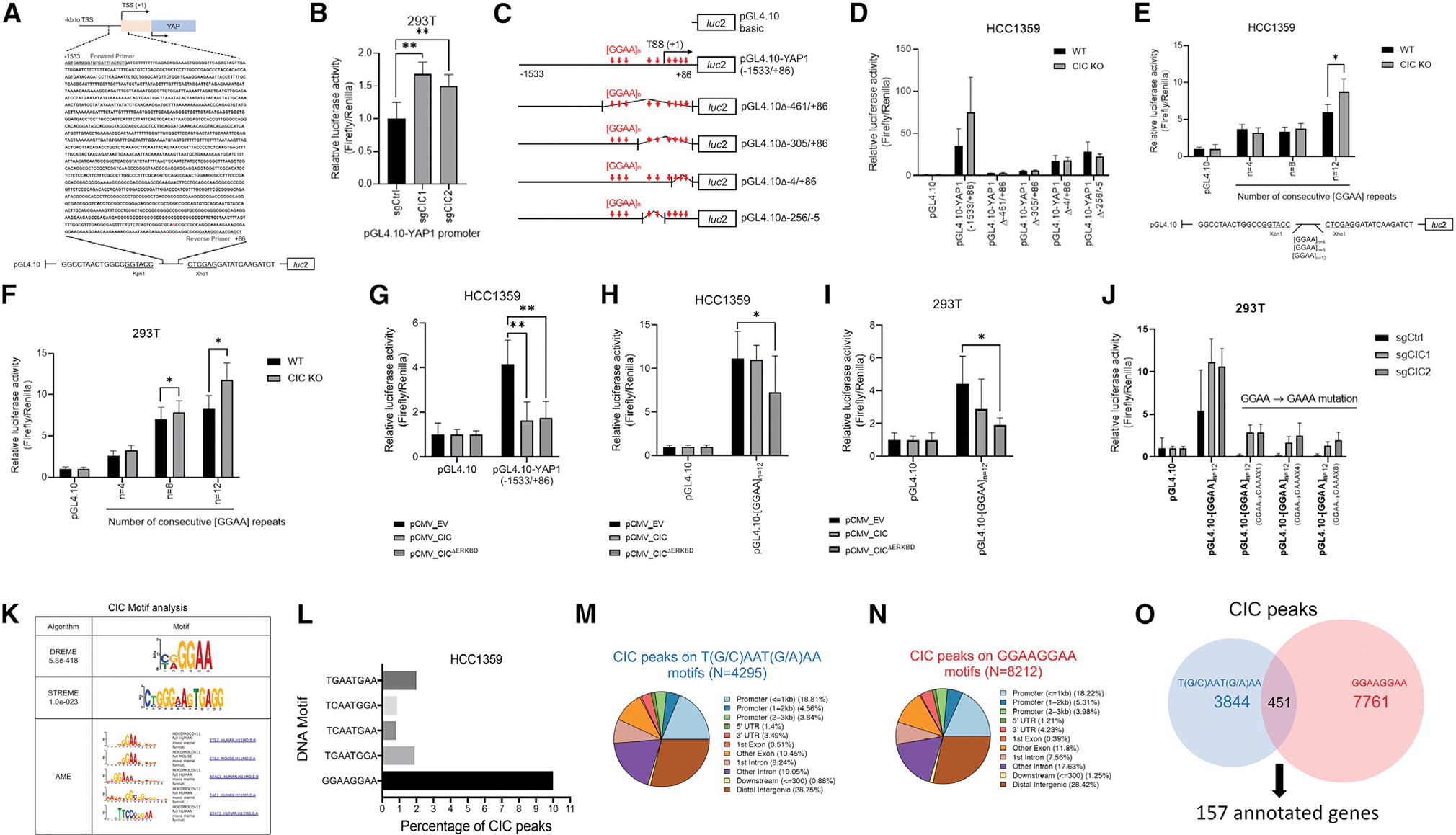
(A) pGL4.10 reporter construct containing the genomic sequence (−1,533 to +86) of YAP1 RE occupied by CIC.
(B) Relative pGL4.10-YAP1 activity in HEK293Ts expressing sgCtrl, sgCIC1, or sgCIC2. **p < 0.01.
(C) Control and mutant pGL4.10 with associated GGAA sites.
(D) Relative pGL4.10-YAP1 activity in HCC1359s expressing either control or a mutant pGL4.10 Luc construct ± CIC (CICWT or CIC KO).
(E) Relative Luc activity of pGL4.10 constructs containing GGAA repeats (n = 4, n = 8, n = 12) in HCC1359s comparing CICWT and CIC KO. *p < 0.05.
(F) Relative Luc activity of pGL4.10 constructs containing GGAA repeats (n = 4, n = 8, n = 12) in HEK293Ts comparing CICWT and CIC KO. *p < 0.05.
(G) Relative Luc activity of the pGL4.10-YAP1 (−1,533/+86) and pGL4.10 control in HCC1359s expressing CICWT or CICΔERKBD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
(H and I) Relative Luc activity of the pGL4.10-[GGAA]n=12 and pGL4.10 control in HCC1359 cells (H) or HEK293Ts (I) overexpressing CICWT or CICΔERKBD compared with EV. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
(J) Relative Luc activity of the pGL4.10-[GGAA]n=12 constructs containing GGAA→GAAA mutation repeats (n = 1, n = 4, n = 8) in HEK293Ts expressing sgCtrl, sgCIC1, or sgCIC2.
(K) DREME, STREME, and AME analysis in HCC1359s identify GGAA sequences as putative CIC-binding sites.
(L) % of total CIC peaks in HCC1359s that align to [GGAA]n (n ≥ 2, designated as GGAAx2+ thereafter) and T(G/C)AAT(G/A)AA DNA motifs.
(M and N) % of T(G/C)AAT(G/A)AA (M) or GGAAx2+ (N) associated CIC peaks at genomic regions in HCC1359s.
(O) Venn diagram comparing CIC peaks at T(G/C)AAT(G/A)AA or GGAAx2+ DNA motifs; 451 shared peaks mapping to 157 genes.
Error bars represent SD.
