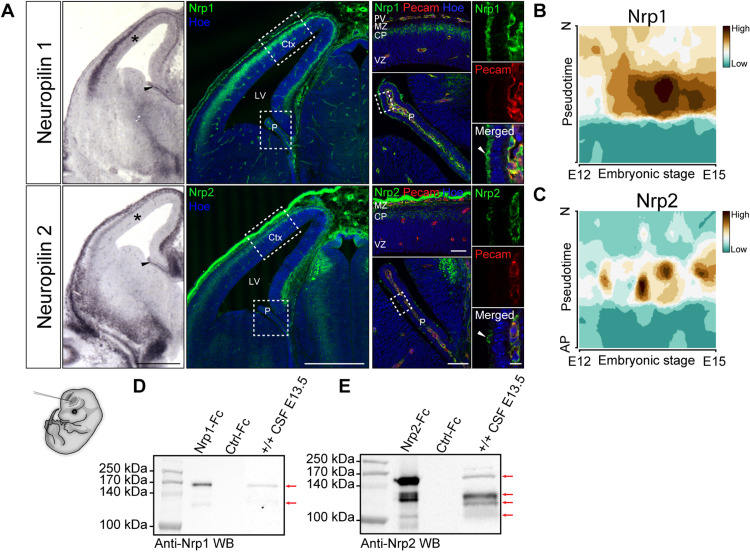
Fig. 2. Neuropilins are expressed in the CP, the cortical plate, and other brain-surrounding tissues and released in the CSF.
(A) In situ hybridization and immunolabeling of Nrp1 and Nrp2 on embryonic brain sections at E13.5. Expression of the class 3 Sema receptors was detected in the nascent CP (black arrowheads), the cortical plate, and meninges. No signal was detected in the cortical ventricular zone (asterisks). Higher magnifications of the cortex and CP colabeled with anti-Pecam highlight Nrp1/2 expression in endothelial cells of the CP and the perineural vascular plexus. The white arrowheads point to the Nrp1/Nrp2 protein signal at the apical border of epithelial cells in the developing CP. High magnifications of the choroid plexi are shown right. (B and C) Single-cell transcriptome analysis of embryonic cortical cells shows that cortical progenitor cells express neither Nrp1 (B) nor Nrp2 (C) between E12 and E15. Pseudotime describes the differentiation from an apical progenitor (AP) cell to a postmitotic neuron (N). (D and E) Immunoblotting on embryonic CSF using antibodies against Nrp1 (D) and Nrp2 (E) indicates that soluble forms of both receptors indicated with arrows are released into the brain fluid. Recombinant Nrp1 and Nrp2 ectodomains fused to Fc fragment were used as positive controls of immunodetection. Scale bars, 500 μm (A, left), 50 μm (A, middle), and 10 μm (A, right). CP, cortical plate; MZ, marginal zone; VZ, ventricular zone; M, meninges; PV, perineural vascular plexus.