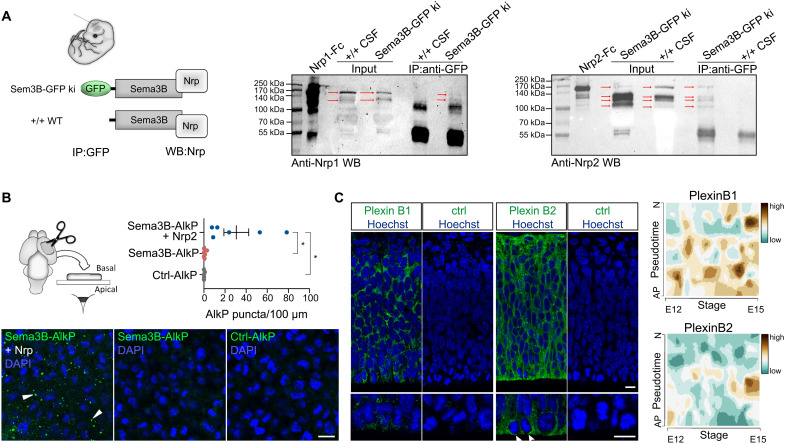
Fig. 3. Sema3s and Nrps form complexes in the embryonic CSF that bind to Plexins at the apical surface of radial glia cells.
(A) Immunoprecipitation (IP) of GFP using CSF of Sema3B-GFP ki/ki mice and WT embryos shows prominent binding of Sema3B-GFP with Nrp2 but rare association with Nrp1 in the CSF. (B) En face binding assays reveal that exposure of cortical tissue to recombinant Sema3B-AlkP and Nrp2-Fc results in binding of the protein complex to the apical surface. In contrast, Sema3B-AlkP alone and control-AlkP do not bind to the apical surface. The histogram depicts the quantification of AlkP puncta. DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. (C) Immunolabeling of PlexinB1 and PlexinB2 on cortical sections at E12.5 shows the expression of these Sema receptors in the developing cortex. Arrowheads point to the accumulation of the PlexinB2 proteins at the apical surface. Single-cell transcriptome analysis of embryonic cortical cells reveals an expression of PlexinB1 and PlexinB2 in apical cortical progenitor cells. Pseudotime describes the differentiation from an apical progenitor (AP) cell to a postmitotic neuron (N) between E12 and E15. Scale bars, 10 μm. Means ± SEM; each dot represents one embryo; paired t test, *P < 0.05.