Figure 3.
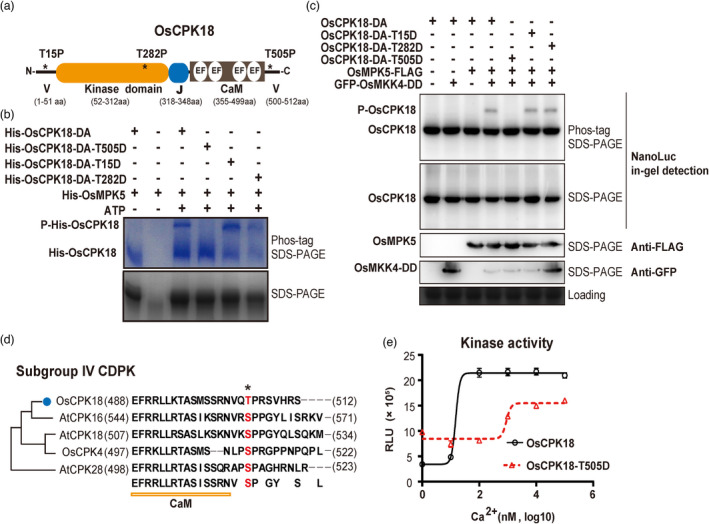
OsMPK5 phosphorylates OsCPK18 T505 and modulates its kinase activity. (a) Schematic illustration of OsCPK18 protein domains. Asterisks (*) denote three MAPK phosphorylation motifs as S/T–P. V, N‐, and C‐terminal variable domains; EF, EF‐hand motif; J, junction peptide; CaM, calmodulin‐like domain for Ca2+ binding. The number at the bottom indicates the position of different protein domains. aa, amino acids. (b) In vitro kinase assays show that His‐OsMPK5 phosphorylated His‐OsCPK18DA, His‐OsCPK18DA‐T15D, and His‐OsCPK18DA‐T282D but not His‐OsCPK18DA‐T505D. The kinase reaction products were analysed using Phos‐tag SDS‐PAGE and regular SDS‐PAGE. The proteins were visualized by Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining. Two phosphorylation reactions without ATP were used as controls to show the mobilities of unphosphorylated proteins. His, polyhistidine tag; P‐His‐OsCPK18, a phosphorylated form of OsCPK18DA recombinant proteins. (c) Activated OsMPK5 phosphorylated OsCPK18 in rice protoplasts. GFP‐tagged OsMKK4DD, FLAG‐tagged OsMPK5, and NanoLuc‐tagged OsCPK18DA with different mutations were coexpressed in rice protoplasts. The rice total proteins were separated by Phos‐tag SDS‐PAGE and regular SDS‐PAGE. The NanoLuc‐tagged proteins were analysed by in‐gel detection (see the Methods), while FLAG‐ and GFP‐tagged proteins were analysed by standard Western blotting. Coomassie Brilliant Blue‐stained gel shows the loading of total protein. P‐OsCPK18, a phosphorylated form of OsCPK18DA‐derived proteins whose mobility was shifted in Phos‐tag SDS–PAGE. (d) Sequence alignment of OsCPK18 and other subgroup IV CDPKs of Arabidopsis and rice. The OsMPK5 phosphorylation site is highlighted in red. The numbers in brackets indicate the positions of the first and last amino acid residues of each protein. (e) Ca2+ sensitivity of OsCPK18 and OsCPK18T505D. The kinase activities were compared using the ADP‐Glo method, which measures the relative amount of ADP produced from phosphorylation reactions. The Histone III‐S protein was used as the substrate in this experiment. RLU, relative luminescent unit. The recombinant protein purification and in vitro kinase reaction were repeated three times with similar results. The data are presented as the mean ± s.d. (n = 3 technical replicates).
