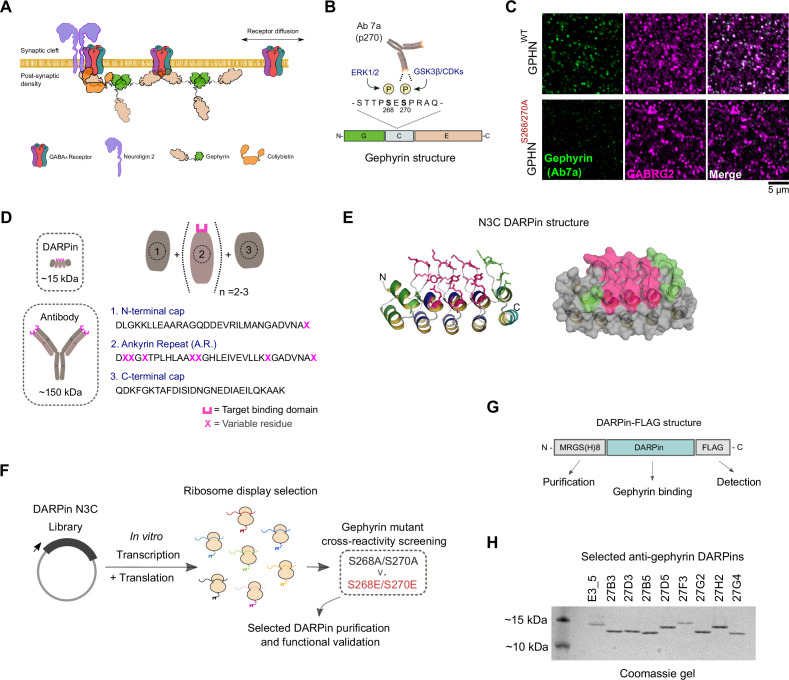
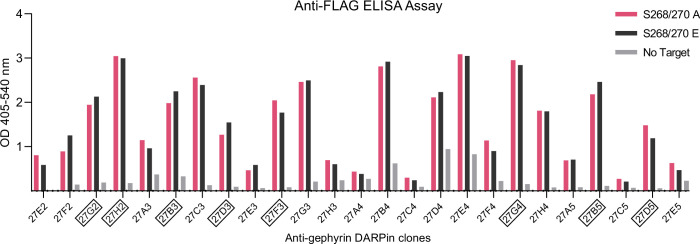
Figure 1. In vitro selection and generation of anti-gephyrin DARPins.
(A) Diagram of gephyrin function at the inhibitory postsynapse via its scaffolding role. (B) Gephyrin domain structure and location of key phosphoserine residues S268 and S270, the commonly used antibody clone for detection of gephyrin (Ab7a) is phospho-S270-specific. (C) The antibody Ab7a does not detect gephyrin clusters colocalized with the γ2 GABAA receptor subunit (GABRG2) in a phospho-null mouse model where S268 and S270 are mutated to alanines. (D) DARPins are an order of magnitude smaller than conventional antibodies and achieve target binding specificity by varying the sequence of ankyrin repeats (A.R.) with variable residues (magenta). (E) DARPin library design, with residues in magenta randomized in the original design and additional residues randomized in the caps (green). An N3C structure is shown with the N-terminal cap as a green ribbon and the C-terminal cap as a cyan ribbon with green side chains. (F) Schematic of anti-gephyrin DARPin selection and screening. (G) Structure of DARPin-FLAG clones used for initial validation experiments contain an N-terminal His8 tag and C-terminal FLAG tag for purification and detection, respectively. (H) Coomassie-stained gel of the nonbinding control (E3_5) and eight anti-gephyrin DARPin binders.