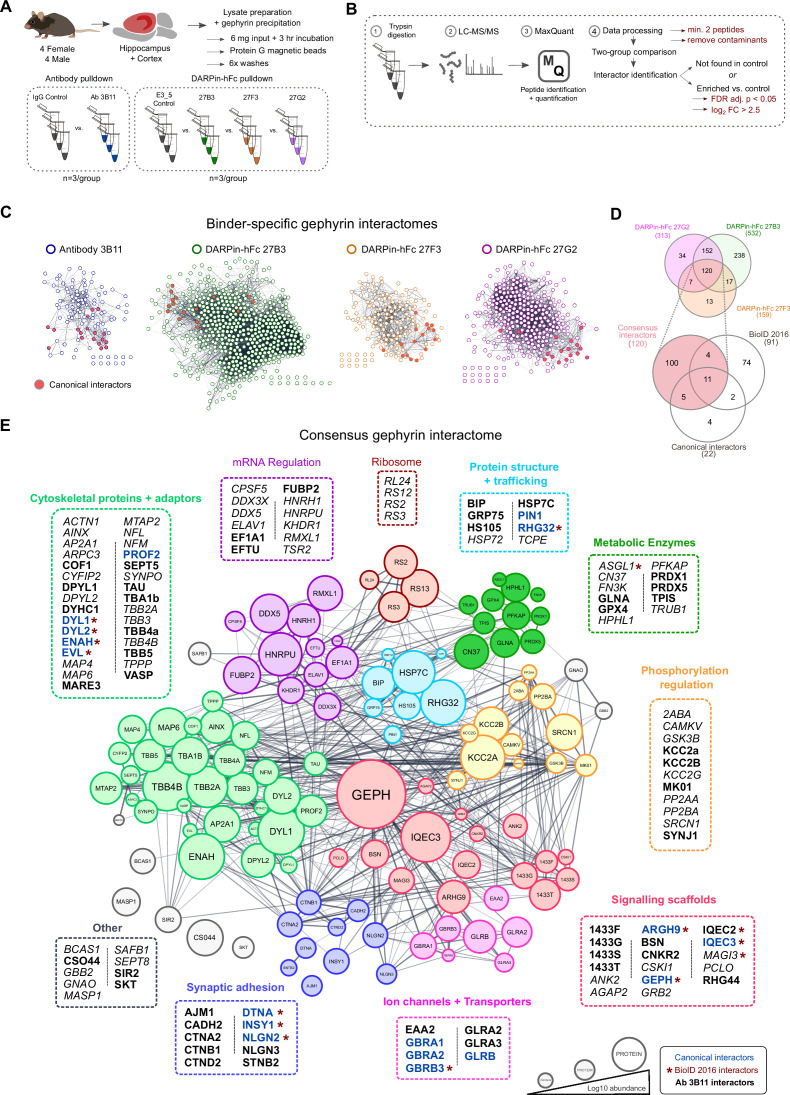
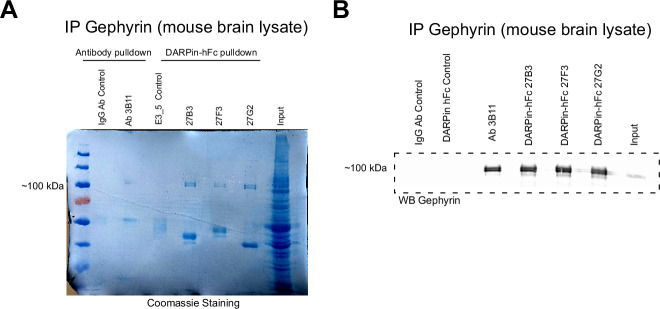
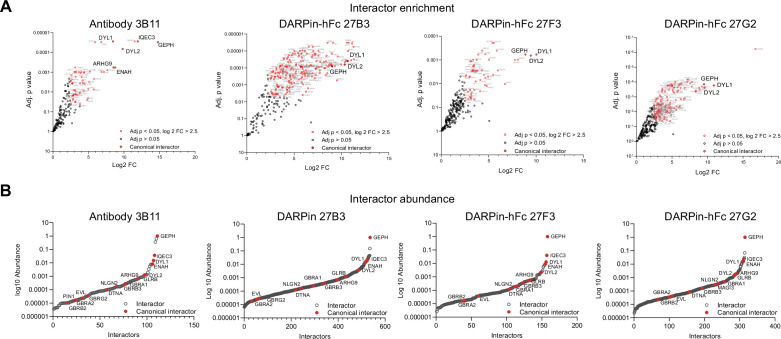
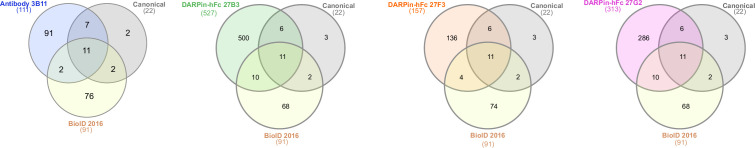
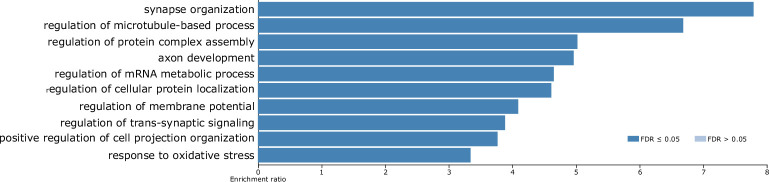
Figure 5. A DARPin-based consensus gephyrin interactome captures both known and novel protein interactors.
A) Mouse brain tissue lysate preparation diagram. (B) Liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) and interactome determination methodology workflow indicating thresholds for consideration of interacting proteins. (C) Scale-free interaction networks (STRING) of gephyrin interactors identified from pulldowns using the commercial antibody 3B11, or DARPin-hFc 27B3, 27F3, and 27G2 compared to control conditions (containing antibody control IgG or the control DARPin-hFc E3_5). Nodes represent unique gephyrin interactors – red nodes indicate known (canonical) gephyrin interactors. (D) Venn diagram of the overlap in identified interactors from gephyrin complexes isolated using different DARPin-hFc clones; bottom indicates coverage compared to an extensive gephyrin interactome determined using BioID labeling (Uezu et al., 2016) and 22 canonical gephyrin interactors identified from the literature. (E) Consensus interactome of proteins identified by all DARPin-hFc clones and colored by protein ontology. Canonical gephyrin interacting proteins are indicated by blue font, and bold font indicates interactors also identified by the antibody clone 3B11. Asterisks indicate proteins previously identified by BioID (Uezu et al., 2016). Italic font indicates interactors exclusively identified by DARPins. Edges connecting protein nodes indicate putative interactions (STRING analysis), and node circle size indicates relative protein abundance averaged across all experiments.