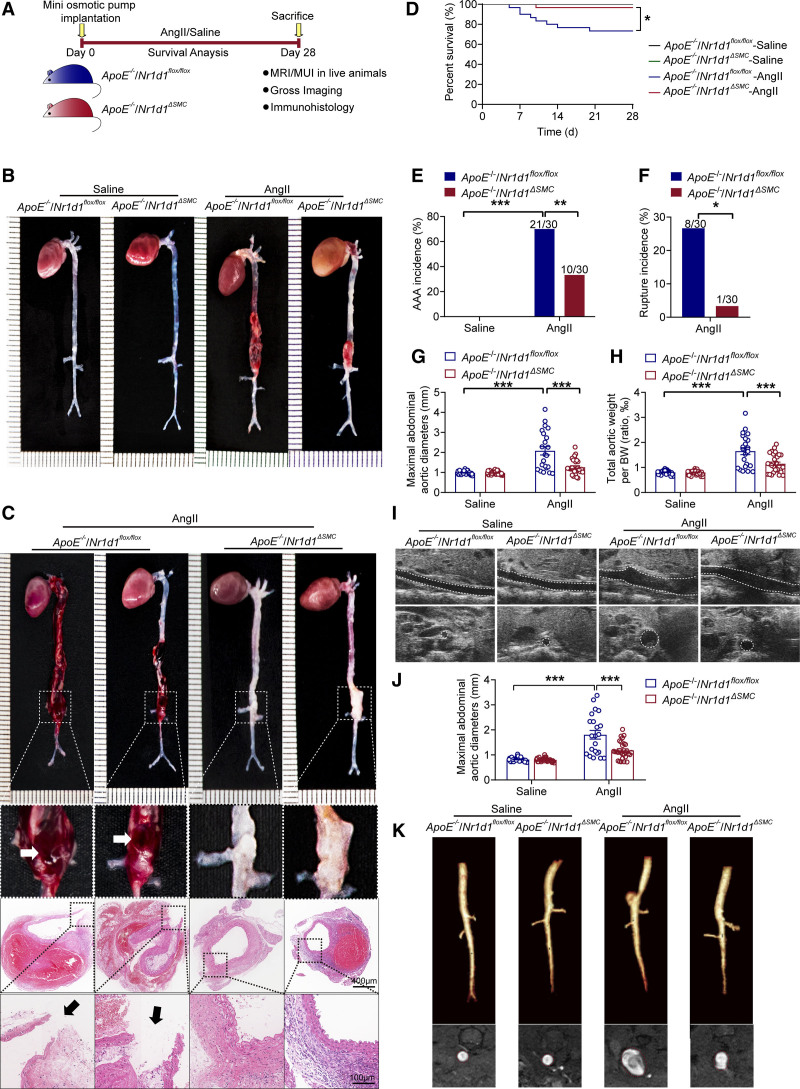
Figure 2.
VSMC-specific NR1D1 deficiency represses AngII-induced AAA formation. A, Schematic protocol: ApoE−/−/Nr1d1flox/flox and ApoE−/−/Nr1d1ΔSMC mice were subcutaneously injected with saline or AngII by a mini osmotic pump for 28 days (n=30 per group). B, Representative images of the macroscopic features of AAA formation in indicated groups. C, Representative images of macroscopic features and HE staining of crossed-sections of aneurysm ruptures (arrow indicated). D, Survival curves in indicated groups (n=30 per group). Survival data were analyzed by the Kaplan-Meier method and compared using log-rank tests. *P<0.05. E, The incidence of AngII-induced AAA in indicated groups (n=30 per group). Data were analyzed by a Fisher exact test. **P<0.01; ***P<0.001. F, The incidence of AngII-induced aneurysm rupture in indicated groups (n=30 per group). Data were analyzed by a Fisher exact test. *P<0.05. G and H, Quantification of the maximal diameter of suprarenal abdominal aortas measured by a Digital Vernier Caliper and total aortic weight/BW in indicated groups (n=22–30 per group). Data were analyzed by 2-way ANOVA followed by the Bonferroni post hoc test. ***P<0.001. I, Representative images of abdominal aortas visualized by MUI using the B mode in indicated groups. J, Quantification of the maximal diameter of suprarenal abdominal aortas measured by MUI using the B mode in indicated groups (n=22–30 per group). Data were analyzed by 2-way ANOVA followed by the Bonferroni post hoc test. ***P<0.001. K, Representative images of abdominal aortas visualized by MRI in indicated groups. Top, Abdominal aortas visualized using 3-dimensional time of flight fast low angle shot sequence (TOF-3D-Flash). Bottom, Abdominal aortas visualized by T2-weighted, PD-weighted imaging with multiple-echo multishot sequence (MEMS-PD-T2). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. AAA indicates abdominal aortic aneurysm; AngII, angiotensin II; BW, body weight; EVG staining, elastin van Gieson staining; HE staining, hematoxylin and eosin staining; MUI, micro-ultrasound imaging; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; NR1D1, nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group D member 1; and SMC, smooth muscle cell.