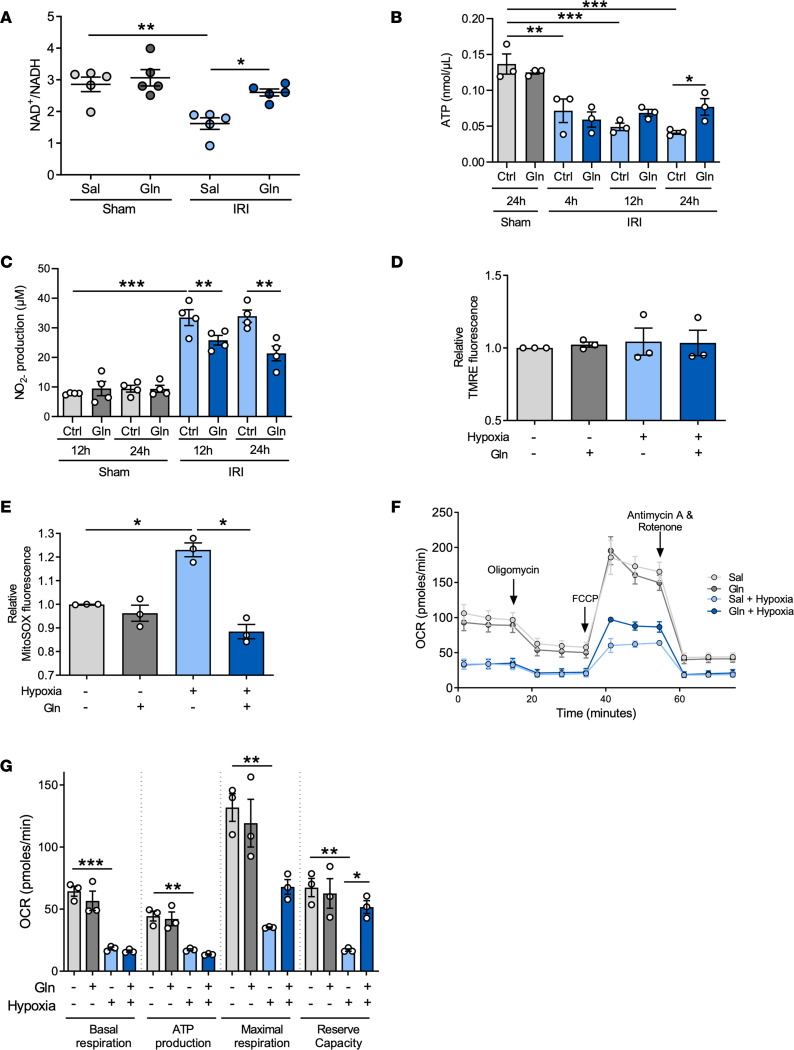
Figure 5. Glutamine supports mitochondrial respiration during oxidative stress.
WT mice were subjected to sham or IRI surgery and received glutamine or saline. NAD+/NADH ratio (A, n = 5), ATP concentration (B, n = 3), and NO2– concentration (C, n = 4) were detected in kidney suspensions 24 hours after IRI by colorimetric assays. TECs were treated with glutamine or saline and subsequently subjected to hypoxic (1% O2) conditions for 24 hours. The mitochondrial membrane potential was assessed by TMRE fluorescence detection (D, n = 3). Mitochondrial ROS production was detected to assess oxidative stress (E, n = 3). Mitochondrial respiration was assessed using the Seahorse XF24 Flux Analyzer. The oxygen consumption rate (OCR) to analyze mitochondrial respiration was measured using the Mito Stress Kit (F and G; n = 3). Mean ± SEM; 1-way ANOVA. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.005; ***P < 0.001. FCCP, carbonyl cyanide-p-trifluoromethoxyphenylhydrazone.