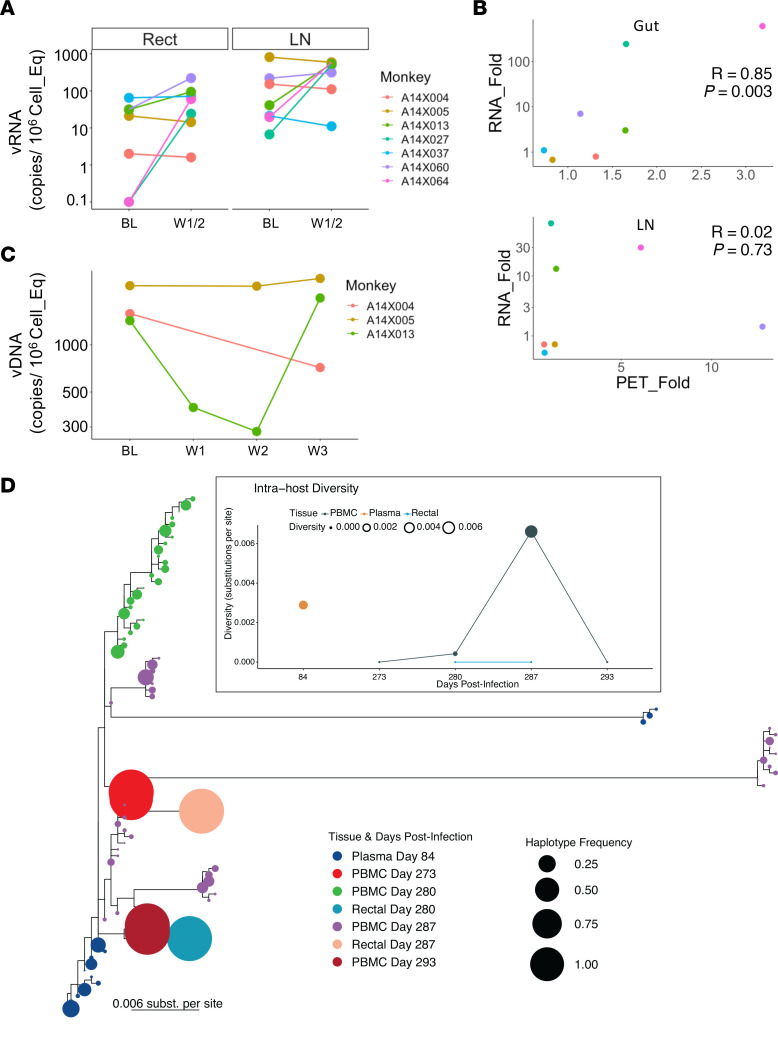
Figure 4. Increased PET signal corresponds to increased vRNA.
(A) Copies of cell-associated unspliced vRNA normalized on 106 cells diploid genome equivalent are shown for colorectal biopsies and LNAs before and after galunisertib treatment. Data from BL and postgalunisertib W1/2 were compared using Wilcoxon matched pairs nonparametric test, and the differences were nonsignificant with α > 0.05. (B) The correlation between the fold increase in SUVtot for the gut (above) and LN (below) and the fold increase in vRNA copies in rectal biopsies and FNAs (only 1 of the axillary LNs was sampled) are shown. Pearson’s correlation coefficient and P values are indicated in each graph. (C) Copies of vDNA per 106 cells equivalent are shown for the PBMCs of the 3 animals that were treated with galunisertib for 2 weeks. W3 time point represents a sample collected 7 days after the last galunisertib administration. No statistical test was performed. (D) Intrahost viral quasispecies evolution before and after galunisertib treatment in A14X013 is shown. Inferred maximum likelihood (ML) tree with quasispecies within the same host in PBMCs, rectal tissues, and blood samples using deep sequencing of the gag gene. Circles at the tips represent each haplotype and are colored by time postinfection and sample type (D84 is plasma right before ART initiation; D273 is PBMC on the day of first galunisertib treatment, collected before treatment; D280-287-290 represent 7, 14, and 20 days after galunisertib initiation). Circle size indicates the frequency of the haplotype in the quasispecies. Insert represents the spatiotemporal evolution of the viral population diversity at each compartment and time point. Both y axis and circle size indicate diversity of quasispecies, and data from the same sample type are connected by lines. Intrahost viral diversity was calculated as weighted average of pairwise distances between every haplotype weighted by their frequency in the population in substitutions per site.